Primary Tubercular Sialadenitis - A Diagnostic Dilemma
- PMID: 30783598
- PMCID: PMC6368988
Primary Tubercular Sialadenitis - A Diagnostic Dilemma
Abstract
Introduction: Involvement of the salivary glands in tuberculosis is rare, even in countries where tuberculosis is endemic. It can occur by systemic dissemination from a distant focus or, less commonly, as primary involvement. This article focuses on its myriad clinical presentations that pose a diagnostic challenge to the clinician. We discuss the schema of investigations required to confirm the diagnosis and the limitations faced in the low-cost setting of a developing country.
Materials and methods: Medical records, including history, physical examination and imaging findings, and the results of cytological, microbiological and histopathological studies of patients diagnosed with primary tubercular sialadenitis were retrieved and analyzed.
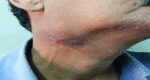
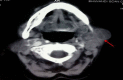
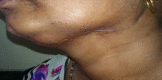
Results: Seven patients were treated over a 2-year period. The most common mode of presentation was a painless mass of the involved gland in four patients. One patient each presented with chronic non-obstructive sialadenitis, sialolithiasis, and acute suppurative sialadenitis. Fine needle aspiration cytology was diagnostic in five out of seven cases (71.4%), while mycobacterial culture was positive in two patients (28.6%). In one patient, a diagnosis could only be reached on histopathological examination of the resected gland.
Conclusion: We recommend cytology studies, acid-fast bacilli staining, and mycobacterial culture as the initial investigation on the aspirate in suspected patients, while polymerase chain reaction should be reserved for negative cases. A high index of suspicion, early diagnosis, and timely institution of anti-tuberculosis treatment is essential for establishing cure. The role of surgery in diagnosed cases of tuberculosis is limited.
Keywords: Parotid gland; Salivary fistula; Salivary gland calculi; Sialadenitis; Submandibular gland; Tuberculosis.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2015. [Accessed: October 2015]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/191102/1/9789241565059_eng.pdf?....
-
- Kumar SP, Rajesh Kumar P. Primary Tuberculosis of Submandibular Gland Presenting as Dental Abscess. J Otol Rhinol. 2013;2:2.
-
- Gupta KB, Yadav SPS, Sarita , Manchanda M. Primary pharyngeal tuberculosis. Lung India. 2005;22:127–9.
-
- Khan AK, Khan NA, Maqbool M. Otorhinolaryngological manifestation of tuberculosis. JK Sci J Med Ed Res. 2002;4(3):115–18.
-
- Kasim KS, Namavar E, Yunus MRM. A rare case of primary tuberculosis of the submandibular gland. Egypt J Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci. 2015;16:87–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
