The 1470 nm diode laser with an intralesional fiber device: a proposed solution for the treatment of inflamed and infected keloids
- PMID: 30783604
- PMCID: PMC6376646
- DOI: 10.1186/s41038-019-0143-6
The 1470 nm diode laser with an intralesional fiber device: a proposed solution for the treatment of inflamed and infected keloids
Abstract
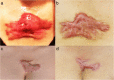
Background: Keloids are the result of abnormal wound healing and often are subject to infections and recurrent inflammation. We present a study conducted with a 1470 nm diode laser using an intralesional optical fiber device for the treatment of inflamed keloid scars. We evaluate its efficacy as a novel alternative method to decrease keloid infection and inflammation.
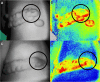
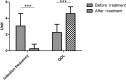
Methods: The patients who underwent 1470 nm laser treatment from February 2016 to February 2018 at the plastic and reconstructive surgery department of the Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University with keloid accompanying serious local infection and fester were included. Patients took curative effect evaluation before and 1 year after the treatment. The test items included infection frequency in each year; pain, by visual analogue scale (VAS); itch, using VAS; quality of life (QOL), using QOL scale; and blood supply, using PeriCam PSI.
Results: A total of 19 patients (mean age 35.21 years, range 11-66) with history of inflamed keloids with episodes of infection or abscess were enrolled. Patients underwent to a 1470 nm laser therapy for average of 1.16 times. After treatment, infection frequency and blood supply in keloids were reduced (p < 0.001). Pain, itching, and QOL were improved (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The present study shows that 1470 nm fiber laser treatment could improve inflamed keloids fairly well by decreasing inflammation, and a relative stabilization of collagen composition. Therefore, it is an effective minimally invasive scar therapy, but further studies are essential to confirm the present results.
Keywords: 1470 nm; Diode laser; Fiber laser; Hypertrophic scars; Keloid scars.
Conflict of interest statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki stated in 1964. The study protocol was agreed by the local ethics committee of the Jiao Tong University-Ninth People’s Hospital of Shanghai. Every patient signed written informed consent.All presentations of case reports in this article have consent for publication.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

