Inhaled steroids associated with decreased macrophage markers in nonasthmatic individuals with sickle cell disease in a randomized trial
- PMID: 30783732
- PMCID: PMC7522666
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-019-03635-9
Inhaled steroids associated with decreased macrophage markers in nonasthmatic individuals with sickle cell disease in a randomized trial
Abstract
Inhaled mometasone was shown to improve pain scores and decrease soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule (sVCAM) concentration in a randomized controlled trial of nonasthmatic patients with sickle cell disease. We sought to explore potential changes in systemic inflammation as a mechanism underlying this effect. Serum samples from 41 trial participants (15 placebo- and 26 mometasone-treated) were analyzed using a 92 inflammatory marker panel at baseline and after 8 weeks of mometasone therapy. Individual marker analysis and correlation analysis were conducted. Adjusted for age, the mometasone-treated group decreased the concentration of CXCL9, CXCL11, CD40, IL-10, and IL-18 relative to placebo-treated participants. Hierarchical clustering and correlation analysis identified additional evidence for a decrease in cytokines linking to macrophage signaling and migration. There was no statistically significant change in markers of asthma and allergy, indicating that the improvement was unlikely mediated by modulation of occult reactive airway disease. This analysis of inflammatory markers suggests that decrease in macrophage activity may be involved in the mediation of the clinical benefit seen with use of inhaled mometasone in nonasthmatic patients with sickle cell disease.Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02061202.
Keywords: Hemoglobinopathies; Inhaled corticosteroids; Macrophage activation; Sickle cell disease.
Figures
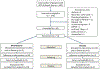
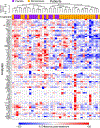
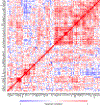
References
-
- Leikin SL, Gallagher D, Kinney TR, Sloane D, Klug P, Rida W (1989) Mortality in children and adolescents with sickle cell disease. Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease. Pediatrics 84 (3):500–508 - PubMed
-
- Pritchard KA Jr., Feroah TR, Nandedkar SD, Holzhauer SL, Hutchins W, Schulte ML, Strunk RC, Debaun MR, Hillery CA (2012) Effects of experimental asthma on inflammation and lung mechanics in sickle cell mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 46 (3):389–396. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0097OC - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

