Hepatitis E virus strains infecting Swedish domestic pigs are unique for each pig farm and remain in the farm for at least 2 years
- PMID: 30784199
- PMCID: PMC6850098
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.13153
Hepatitis E virus strains infecting Swedish domestic pigs are unique for each pig farm and remain in the farm for at least 2 years
Abstract
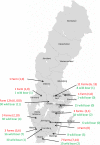
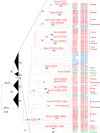
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotype 3 (HEV3) is distributed globally and infects both humans and animals, mainly domestic pigs and wild boars, which are the major reservoirs. In this study, the prevalence of HEV among Swedish pigs was investigated by HEV RNA analysis in 363 faecal samples from 3-month-old piglets sampled twice (2013 and 2014) in 30 Swedish pig farms. Four different types of farms were investigated; organic, conventional closed (keeping the sow), satellites in a sow pool (conventional farms sharing sows) and conventional non-closed farms (purchasing gilts). More than two-thirds (77%) of the farms had HEV-infected pigs. HEV RNA was found in faeces from 79 pigs (22%). Partial ORF1 could be sequenced in 46 strains. Phylogenetic analysis revealed a unique HEV3 strain for each farm. Strains sampled more than a year apart from the same farm were closely related, indicating that the same HEV strain is present for several years on the farm. Despite that only 4% of the Swedish pig farms were investigated, two farms had strains similar to those from humans, another had strains similar to wild boar HEV. The uniqueness of strains from each farm indicates a possibility to identify a source of infection down to farm level. This knowledge may be used by the farms to investigate the effectiveness of good hygiene routines to reduce the amount of HEV and thus the infection risk in the farm, and for Swedish public health authorities to identify cases of HEV transmissions from consumption of uncooked pork.
Keywords: HEV; HEV RNA; anti-HEV; zoonosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases Published by Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetically similar hepatitis E virus strains infect both humans and wild boars in the Barcelona area, Spain, and Sweden.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019 Mar;66(2):978-985. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13115. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019. PMID: 30597741
-
Long-term surveillance for hepatitis E virus in an Italian two-site farrow-to-finish swine farm.Zoonoses Public Health. 2021 Aug;68(5):474-482. doi: 10.1111/zph.12837. Epub 2021 May 2. Zoonoses Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33934531
-
Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in humans, pigs and wild boars in Sweden.Epidemiol Infect. 2011 Mar;139(3):361-71. doi: 10.1017/S0950268810001342. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Epidemiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 20546635
-
Hepatitis E and Potential Public Health Implications from a One-Health Perspective: Special Focus on the European Wild Boar (Sus scrofa).Pathogens. 2024 Sep 27;13(10):840. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100840. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis E virus: animal reservoirs and zoonotic risk.Vet Microbiol. 2010 Jan 27;140(3-4):256-65. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.03.017. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Vet Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19361937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis A Virus and Hepatitis E Virus as Food- and Waterborne Pathogens-Transmission Routes and Methods for Detection in Food.Viruses. 2023 Aug 12;15(8):1725. doi: 10.3390/v15081725. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study.Animals (Basel). 2021 Oct 25;11(11):3050. doi: 10.3390/ani11113050. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827782 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Shedding in Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Apr 20;12(9):1063. doi: 10.3390/ani12091063. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565491 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Strains from Pigs Farmed in Eight European Countries between 2020 and 2022.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023 Dec 7;2023:2806835. doi: 10.1155/2023/2806835. eCollection 2023. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023. PMID: 40303777 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct distribution of HEV-3 subtypes across humans, animals, and environmental waters in Sweden.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2488188. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2488188. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 40166982 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

