Bone Morphogenetic Protein-6 Attenuates Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Bone Loss
- PMID: 30784225
- PMCID: PMC6525561
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.18-0150
Bone Morphogenetic Protein-6 Attenuates Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Bone Loss
Abstract
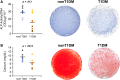
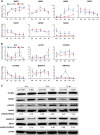
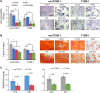
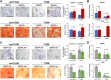
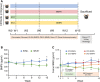
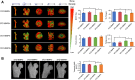
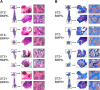
Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) often suffer from osteopenia or osteoporosis. Although most agree that T1DM-induced hyperglycemia is a risk factor for progressive bone loss, the mechanisms for the link between T1DM and bone loss still remain elusive. In this study, we found that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) isolated from T1DM donors were less inducible for osteogenesis than those from non-T1DM donors and further identified a mechanism involving bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP6) that was produced significantly less in BMSCs derived from T1DM donors than that in control cells. With addition of exogenous BMP6 in culture, osteogenesis of BMSCs from T1DM donors was restored whereas the treatment of BMP6 seemed not to affect non-T1DM control cells. We also demonstrated that bone mineral density (BMD) was reduced in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice compared with that in control animals, and intraperitoneal injection of BMP6 mitigated bone loss and increased BMD in diabetic mice. Our results suggest that bone formation in T1DM patients is impaired by reduction of endogenous BMP6, and supplementation of BMP6 enhances osteogenesis of BMSCs to restore BMD in a mouse model of T1DM, which provides insight into the development of clinical treatments for T1DM-assocaited bone loss. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2019;8:522-534.
Keywords: Bone loss; Bone morphogenetic protein-6; Hyperglycemia; Mesenchymal stem cell; Osteogenesis; Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
© 2019 The Authors. Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
M.W.S. declared Intellectual property rights with Zimmer‐Biomet. W.‐J.L. declared financial relationship as editor of an academic book for a publisher group. The other authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Group SfDiYS , Liese AD, D'Agostino RB Jr et al. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: Prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics 2006;118:1510–1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

