Mass Spectrometric Imaging Reveals Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Bioactive Lipids in Arteries Undergoing Restenosis
- PMID: 30784274
- PMCID: PMC6481175
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00941
Mass Spectrometric Imaging Reveals Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Bioactive Lipids in Arteries Undergoing Restenosis
Abstract
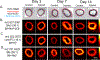
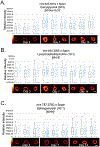
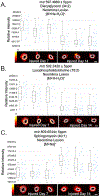
Restenosis, or renarrowing of the arterial lumen, is a common recurrent disease following balloon angioplasty and stenting treatments for cardiovascular disease. A major technical barrier for deciphering restenotic mechanisms is the dynamic, spatial profiling of bioactive lipids in the arterial wall, especially in small animals. Here, applying matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI), we conducted the first lipidomic study of temporal-spatial profiling in a small animal model of angioplasty-induced restenosis. Cross sections were collected 3, 7, and 14 days after balloon angioplasty of rat carotid arteries. MALDI-MSI analyses showed that diacylglycerols (DAGs), signaling lipids associated with restenosis, and lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs), whose function was uncharacterized in restenosis, dramatically increased at postangioplasty day 7 and day 14 in the neointimal layer of balloon-injured arteries compared to uninjured controls. In contrast, sphingomyelins (SMs) did not increase, but rather decreased at day 3, day 7, and day 14 in injured arteries versus the uninjured control arteries. These results revealed previously unexplored distinct temporal-spatial lipid dynamics in the restenotic arterial wall. Additionally, we employed time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) tandem MS imaging for both molecular identification and imaging at high spatial resolution. These imaging modalities provide powerful tools for unraveling novel mechanisms of restenosis involving lipids or small signaling molecules.
Keywords: MALDI-MSI; TOF-SIMS; lipids; neointima; restenosis; vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
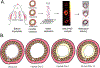

References
-
- Heron M; Anderson RN Changes in the Leading Cause of Death: Recent Patterns in Heart Disease and Cancer Mortality. NCHS Data Brief 2016, No. 254, 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Cassese S; Byrne RA; Tada T; Pinieck S; Joner M; Ibrahim T; King LA; Fusaro M; Laugwitz KL; Kastrati A Incidence and predictors of restenosis after coronary stenting in 10 004 patients with surveillance angiography. Heart 2014, 100 (2), 153–9. - PubMed
-
- Wei GL; Krasinski K; Kearney M; Isner JM; Walsh K; Andres V Temporally and spatially coordinated expression of cell cycle regulatory factors after angioplasty. Circ. Res 1997, 80 (3), 418–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

