Classic and Nonclassic Renin-Angiotensin Systems in the Critically Ill
- PMID: 30784605
- PMCID: PMC7125612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2018.11.002
Classic and Nonclassic Renin-Angiotensin Systems in the Critically Ill
Abstract
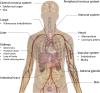
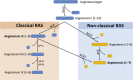
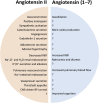
Classic and nonclassic renin-angiotensin systems (RAS) are 2 sides of an ubiquitous endocrine/paracrine cascade regulating blood pressure and homeostasis. Angiotensin II and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels are associated with severity of disease in the critically ill, and are central to the physiology and the pathogenesis of circulatory shock. Angiotensin (1-7) and ACE2 act as an endogenous counterregulatory arm to the angiotensin II/ACE axis. The tissue-based RAS has paracrine effects dissociated from those of the circulating RAS. Exogenous angiotensin II or ACE2 may improve the outcome of septic shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome, respectively.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Acute respiratory distress syndrome; Angiotensin; Angiotensin-converting enzyme; Inflammation; Renin; Sepsis; Septic shock.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Khanna A., English S.W., Wang X.S., et al. Angiotensin II for the treatment of vasodilatory shock. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):419–430. - PubMed
-
- Cruces P., Diaz F., Puga A., et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism is associated with severe hypoxemia in pediatric ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(1):113–119. - PubMed
-
- Annoni F., Orbegozo Cortés D., Irazabal M., et al. Angiotensin converting enzymes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2015;3(1):A91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

