The risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30785930
- PMCID: PMC6382168
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212574
The risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis
Abstract
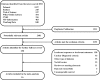
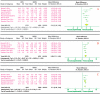
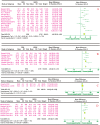
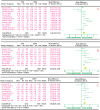
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), the most common chronic complication of diabetes, has become an important public health crisis worldwide. Given that DPN is extremely difficult to treat, determining its risk factors and controlling it at an early stage is critical to preventing its serious consequences and the burden of social disease. Current studies suggest that the risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy are the duration of diabetes, age, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), diabetic retinopathy (DR), smoking, and body mass Index (BMI). However, most of the aforementioned studies are cross-sectional, and the sample sizes are very limited, so the strength of causal reasoning is relatively low. The current study systematically evaluated DPN's influencing factors in patients with type 2 diabetes using evidence-based medicine. Overall, 16 included studies (14 cross-sectional studies and 2 case-control studies including 12,116 cases) that conformed to the present criteria were included in the final analysis. The results suggested that the duration of diabetes (MD 2.5, 95% CI 1.71~3.29), age (MD 4.00, 95% CI 3.05~4.95), HbA1c (MD 0.48, 95% CI 0.33~0.64), and DR (OR 2.34, 95% CI 1.74~3.16) are associated with significantly increased risks of DPN among diabetic patients, while BMI, smoking, total triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) did not indicate any risks of increasing DPN. The findings provide a scientific basis for a further understanding of the causes of type 2 diabetes complicated with peripheral neuropathy and the improvement of preventive strategies. The next step is to conduct further high-quality prospective cohort studies to validate this paper's findings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


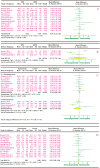
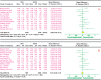

References
-
- Wang H, Hu R, Wu H, Yu M. [Progress in reporting incidence of type 2 diabetes]. Zhejiang Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2016;28(1):37–9,57.
-
- Argoff CE, Cole BE, Fishbain DA, Irving GA. Diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: clinical and quality-of-life issues. Mayo Clinic proceedings. 2006;81(4 Suppl):S3–11. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

