The plastidial metabolite 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate modulates defence responses against aphids
- PMID: 30786032
- PMCID: PMC6850158
- DOI: 10.1111/pce.13538
The plastidial metabolite 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate modulates defence responses against aphids
Abstract
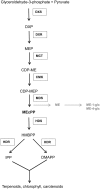
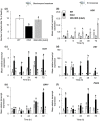
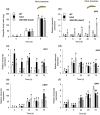
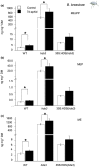
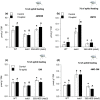
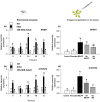
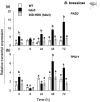
Feeding by insect herbivores such as caterpillars and aphids induces plant resistance mechanisms that are mediated by the phytohormones jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA). These phytohormonal pathways often crosstalk. Besides phytohormones, methyl-D-erythriol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP), the penultimate metabolite in the methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway, has been speculated to regulate transcription of nuclear genes in response to biotic stressors such as aphids. Here, we show that MEcPP uniquely enhances the SA pathway without attenuating the JA pathway. Arabidopsis mutant plants that accumulate high levels of MEcPP (hds3) are highly resistant to the cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae), whereas resistance to the large cabbage white caterpillar (Pieris brassicae) remains unaltered. Thus, MEcPP is a distinct signalling molecule that acts beyond phytohormonal crosstalk to induce resistance against the cabbage aphid in Arabidopsis. We dissect the molecular mechanisms of MEcPP mediating plant resistance against the aphid B. brassicae. This shows that MEcPP induces the expression of genes encoding enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of several primary and secondary metabolic pathways contributing to enhanced resistance against this aphid species. A unique ability to regulate multifaceted molecular mechanisms makes MEcPP an attractive target for metabolic engineering in Brassica crop plants to increase resistance to cabbage aphids.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; aphid resistance; indole glucosinolates; phloem-sucking herbivores; phytohormone signalling; retrograde signalling; secondary metabolites.
© 2019 The Authors Plant, Cell & Environment Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The plastidial retrograde signal methyl erythritol cyclopyrophosphate is a regulator of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk.J Exp Bot. 2016 Mar;67(5):1557-66. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv550. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 26733689 Free PMC article.
-
Density-dependent interference of aphids with caterpillar-induced defenses in Arabidopsis: involvement of phytohormones and transcription factors.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan;56(1):98-106. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu150. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25339349
-
Towards global understanding of plant defence against aphids--timing and dynamics of early Arabidopsis defence responses to cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae) attack.Plant Cell Environ. 2008 Aug;31(8):1097-115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01823.x. Epub 2008 Apr 21. Plant Cell Environ. 2008. PMID: 18433442
-
Biochemistry and molecular biology of Arabidopsis-aphid interactions.Bioessays. 2007 Sep;29(9):871-83. doi: 10.1002/bies.20624. Bioessays. 2007. PMID: 17691101 Review.
-
Plastidial metabolites and retrograde signaling: A case study of MEP pathway intermediate MEcPP that orchestrates plant growth and stress responses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 May;222:109747. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109747. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40073740 Review.
Cited by
-
HDR, the last enzyme in the MEP pathway, differently regulates isoprenoid biosynthesis in two woody plants.Plant Physiol. 2023 May 31;192(2):767-788. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad110. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36848194 Free PMC article.
-
The methylerythritol phosphate pathway as an oxidative stress sense and response system.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 21;15(1):5303. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49483-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38906898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Drought on the Methylerythritol 4-Phosphate (MEP) Pathway in the Isoprene Emitting Conifer Picea glauca.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Oct 9;11:546295. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.546295. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33163010 Free PMC article.
-
Sipha maydis sensitivity to defences of Lolium multiflorum and its endophytic fungus Epichloë occultans.PeerJ. 2019 Dec 18;7:e8257. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8257. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31976166 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxyxylulose 5-Phosphate Synthase Does Not Play a Major Role in Regulating the Methylerythritol 4-Phosphate Pathway in Poplar.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 10;25(8):4181. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084181. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burow, M. , Muller, R. , Gershenzon, J. , & Wittstock, U. (2006). Altered glucosinolate hydrolysis in genetically engineered Arabidopsis thaliana and its influence on the larval development of Spodoptera littoralis . Journal of Chemical Ecology, 32, 2333–2349. 10.1007/s10886-006-9149-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cui, J. P. , Jander, G. , Racki, L. R. , Kim, P. D. , Pierce, N. E. , & Ausubel, F. M. (2002). Signals involved in Arabidopsis resistance to Trichoplusia ni caterpillars induced by virulent and avirulent strains of the phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae . Plant Physiology, 129, 551–564. 10.1104/pp.010815 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

