Nanoparticle Therapy for Vascular Diseases
- PMID: 30786744
- PMCID: PMC6436996
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311569
Nanoparticle Therapy for Vascular Diseases
Abstract
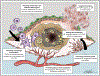
Nanoparticles promise to advance strategies to treat vascular disease. Since being harnessed by the cancer field to deliver safer and more effective chemotherapeutics, nanoparticles have been translated into applications for cardiovascular disease. Systemic exposure and drug-drug interactions remain a concern for nearly all cardiovascular therapies, including statins, antithrombotic, and thrombolytic agents. Moreover, off-target effects and poor bioavailability have limited the development of completely new approaches to treat vascular disease. Through the rational design of nanoparticles, nano-based delivery systems enable more efficient delivery of a drug to its therapeutic target or even directly to the diseased site, overcoming biological barriers and enhancing a drug's therapeutic index. In addition, advances in molecular imaging have led to the development of theranostic nanoparticles that may simultaneously act as carriers of both therapeutic and imaging payloads. The following is a summary of nanoparticle therapy for atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and restenosis and an overview of recent major advances in the targeted treatment of vascular disease.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; nanotechnology; restenosis; thrombosis; vascular diseases.
Figures
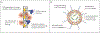
References
-
- The top 10 causes of death. World Health Organization. 2018
-
- Fordyce CB, Roe MT, Ahmad T, et al. Cardiovascular drug development: is it dead or just hibernating? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1567–1582 - PubMed
-
- Smith BR, Gambhir SS. Nanomaterials for In Vivo Imaging. Chem Rev. 2017;117:901–986 - PubMed
-
- Barenholz Y Doxil(R)--the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release. 2012;160:117–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

