Modeling and simulation of phototransduction cascade in vertebrate rod photoreceptors
- PMID: 30786871
- PMCID: PMC6381673
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-019-1048-7
Modeling and simulation of phototransduction cascade in vertebrate rod photoreceptors
Abstract
Background: The activation of phototransduction cascade in rod photoreceptors has been well studied in literature, but there is a lack of a mature kinetic model structure covering both the activation and inactivation processes.
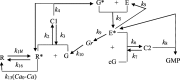
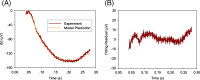
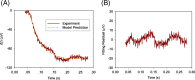
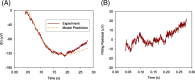
Methods: In this work, a kinetic model structure is developed to describe the major activation and inactivation processes in vertebrate rod photoreceptors with the electroretinogram (ERG) as output. Simulation was performed to validate developed model structure.
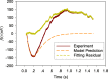
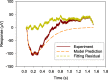
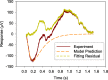
Results: The developed model structure could fit experimental data with small error.
Conclusions: The result indicated that the developed model structure could show the inactivation process of phototransduction cascades in the rod photoreceptors.
Keywords: ERG a wave; Kinetic model structure; Photoreceptor; Phototransduction; Rod.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Arshavsky VY, Lamb TD, Pugh EN. G Proteins and Phototransduction. Annual Review of Physiology. 2002;64:153–87. - PubMed
-
- Armington JC. The electroretinogram (pp. 275–278) New York: Academic Press; 1974.
-
- Constantinides A, Mostoufi N. Numerical methods for chemical engineers with MATLAB applications. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR; 1999.
-
- Einthoven W, Jolly WA. The form and magnitude of the electrical response of the eye to stimulation by light at various intensities. Exp Physiol. 1908;1(4):373–416.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

