In vivo localization of human acetylcholinesterase-derived species in a β-sheet conformation at the core of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30787102
- PMCID: PMC6484111
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006230
In vivo localization of human acetylcholinesterase-derived species in a β-sheet conformation at the core of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
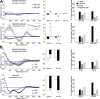
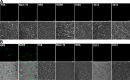
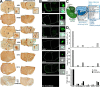
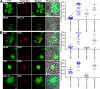
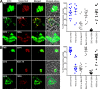
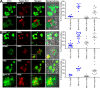
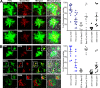
Many neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by amyloid deposition. In Alzheimer's disease (AD), β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides accumulate extracellularly in senile plaques. The AD amyloid cascade hypothesis proposes that Aβ production or reduced clearance leads to toxicity. In contrast, the cholinergic hypothesis argues for a specific pathology of brain cholinergic pathways. However, neither hypothesis in isolation explains the pattern of AD pathogenesis. Evidence suggests that a connection exists between these two scenarios: the synaptic form of human acetylcholinesterase (hAChE-S) associates with plaques in AD brains; among hAChE variants, only hAChE-S enhances Aβ fibrillization in vitro and Aβ deposition and toxicity in vivo Only hAChE-S contains an amphiphilic C-terminal domain (T40, AChE575-614), with AChE586-599 homologous to Aβ and forming amyloid fibrils, which implicates T40 in AD pathology. We previously showed that the amyloid scavenger, insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE), generates T40-derived amyloidogenic species that, as a peptide mixture, seed Aβ fibrillization. Here, we characterized 11 peptides from a T40-IDE digest for β-sheet conformation, surfactant activity, fibrillization, and seeding capability. We identified residues important for amyloidogenicity and raised polyclonal antibodies against the most amyloidogenic peptide. These new antisera, alongside other specific antibodies, labeled sections from control, hAChE-S, hAPPswe, and hAChE-S/hAPPswe transgenic mice. We observed that hAChE-S β-sheet species co-localized with Aβ in mature plaque cores, surrounded by hAChE-S α-helical species. This observation provides the first in vivo evidence of the conformation of hAChE-S species within plaques. Our results may explain the role of hAChE-S in Aβ deposition and aggregation, as amyloidogenic hAChE-S β-sheet species might seed Aβ aggregation.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; acetylcholinesterase (AChE); amyloid-beta (AB); beta-sheet conformation; brain; oligomerization domain; proteolysis; seeding; senile plaques; transgenic mice.
© 2019 Jean et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Heterologous amyloid seeding: revisiting the role of acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2007 Jul 25;2(7):e652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000652. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17653279 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic mice overexpressing human acetylcholinesterase and the Swedish amyloid precursor protein mutation: effect of nicotine treatment.Neuroscience. 2008 Mar 3;152(1):223-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.022. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18164554
-
Pyroglutamation of amyloid-βx-42 (Aβx-42) followed by Aβ1-40 deposition underlies plaque polymorphism in progressing Alzheimer's disease pathology.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 26;294(17):6719-6732. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006604. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30814252 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
[Involvement of beta-amyloid in the etiology of Alzheimer's disease].Brain Nerve. 2010 Jul;62(7):691-9. Brain Nerve. 2010. PMID: 20675873 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Enzyme ChE, cholinergic therapy and molecular docking: Significant considerations and future perspectives.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241289013. doi: 10.1177/03946320241289013. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39367568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antioxidant Activity of Limonene Counteracts Neurotoxicity Triggered byAβ1-42 Oligomers in Primary Cortical Neurons.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;10(6):937. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060937. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207788 Free PMC article.
-
Aducanumab-Hope or Disappointment for Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 22;24(5):4367. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Donepezil Supplementation on Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology and Gut Microbiome in APP/PS1 Mice.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 13;11(9):2306. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092306. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764150 Free PMC article.
-
Donepezil-based rational design of N-substituted quinazolinthioacetamide candidates as potential acetylcholine esterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: in vitro and in vivo studies.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Feb 13. doi: 10.1039/d4md00778f. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40027342 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

