Mouse and human urothelial cancer organoids: A tool for bladder cancer research
- PMID: 30787188
- PMCID: PMC6410883
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1803595116
Mouse and human urothelial cancer organoids: A tool for bladder cancer research
Abstract
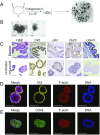
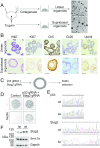
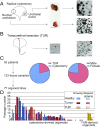
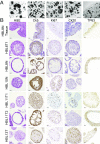
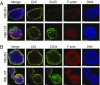
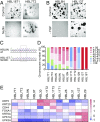
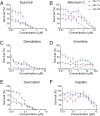
Bladder cancer is a common malignancy that has a relatively poor outcome. Lack of culture models for the bladder epithelium (urothelium) hampers the development of new therapeutics. Here we present a long-term culture system of the normal mouse urothelium and an efficient culture system of human bladder cancer cells. These so-called bladder (cancer) organoids consist of 3D structures of epithelial cells that recapitulate many aspects of the urothelium. Mouse bladder organoids can be cultured efficiently and genetically manipulated with ease, which was exemplified by creating genetic knockouts in the tumor suppressors Trp53 and Stag2. Human bladder cancer organoids can be derived efficiently from both resected tumors and biopsies and cultured and passaged for prolonged periods. We used this feature of human bladder organoids to create a living biobank consisting of bladder cancer organoids derived from 53 patients. Resulting organoids were characterized histologically and functionally. Organoid lines contained both basal and luminal bladder cancer subtypes based on immunohistochemistry and gene expression analysis. Common bladder cancer mutations like TP53 and FGFR3 were found in organoids in the biobank. Finally, we performed limited drug testing on organoids in the bladder cancer biobank.
Keywords: bladder cancer; organoid; urothelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Mouse and Human Urothelial Cancer Organoids: A Tool for Bladder Cancer Research.J Urol. 2019 Oct;202(4):664. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000576984.21354.ad. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31287759 No abstract available.
-
Bladder organoids: a step towards personalised cancer therapy?Transl Androl Urol. 2019 Jul;8(Suppl 3):S300-S302. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.06.10. Transl Androl Urol. 2019. PMID: 31392152 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Establishing and characterization of human and murine bladder cancer organoids.Transl Androl Urol. 2019 Jul;8(Suppl 3):S310-S313. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.06.05. Transl Androl Urol. 2019. PMID: 31392155 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dutch Cancer Registry (NKR) 2018 Available at https://www.cijfersoverkanker.nl/. Accessed February 1, 2018.
-
- Berdik C. Unlocking bladder cancer. Nature. 2017;551:S34–S35. - PubMed
-
- Hermans TJN, et al. Neoadjuvant treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: The past, the present, and the future. Urol Oncol. 2018;36:413–422. - PubMed
-
- Felsenstein KM, Theodorescu D. Precision medicine for urothelial bladder cancer: Update on tumour genomics and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15:92–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

