Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis
- PMID: 30787365
- PMCID: PMC6382780
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-38956-2
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis
Abstract
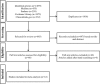
We aimed to assess if GLP-1 agonists are associated with pancreatic cancer. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials with GLP-1 agonists as an intervention was performed. Trial sequential analysis (TSA) was performed to assess if the available information is sufficient to reject this association. Twelve trials met the study criteria, with a total of 36, 397 patients. GLP-1 analogues did not increase the risk for pancreatic cancer when compared to other treatments (OR 1.06; 95% CI 0.67 to 1.67; I2 14%). TSA confirmed that enough patients were randomized and again no association of the medications and pancreatic cancer was observed considering a NNH of 1000 and the short mean follow-up of the included trials (1.7 years). Larger studies with longer duration would be required to exclude a greater NNH and to aside concerns regarding possible influence of study duration and the outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L.G. reports grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), during the conduct of the study; the sponsor had no interference on data extracting, analyses and manuscript writing. L.C.P., D.V.R., S.S.B. and C.B.L. have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Administration, F. a. D. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA investigating reports of possible increased risk of pancreatitis and pre-cancerous findings of the pancreas from incretin mimetic drugs for type 2 diabetes, https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm343187.htm (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous