Preoperative prognostic factors for macular hole surgery: Which is better?
- PMID: 30787530
- PMCID: PMC6380157
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_247_2017
Preoperative prognostic factors for macular hole surgery: Which is better?
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to evaluate the prognostic factors of different optical coherence tomography (OCT) parameters as well as the tamponade used in surgery, on postoperative anatomical and functional success.
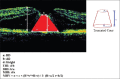
Methods: Twenty-nine eyes of 27 patients were included in this study. A three-port 23-gauge pars plana vitrectomy was performed on all eyes with peeling of the internal limiting membrane by visualization with brilliant blue dye by the same surgeon (E.U). Apical diameter (AD), base diameter (BD), and height (H) were manually measured by the same retina specialist (E.U) with using the software on OCT machine. Macular hole index (MHI), tractional hole index, diameter hole index, and macular hole volume (MHV) were calculated. The correlation between predictive factors and postoperative best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was evaluated.
Results: A statistically significant positive correlation was observed between preoperative BCVA, AD, BD, MHV, and postoperative BCVA scores. A statistically significant negative correlation was observed between preoperative MHI and postoperative BCVA scores (r = -0.676, P = 0.001). The strongest positive correlation was between BD and postoperative BCVA (logMAR) (r = 0.732, P = 0.001). The visual improvement was statistically better in patients treated with C3F8 than SF6.
Conclusion: BD and MHV could be used as a strong predictive OCT parameters of postoperative functional success.
Keywords: Base diameter; macular hole index; macular hole volume; pars plana vitrectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Unsal et al. Preoperative prognostic factors for macular hole surgery: which is better? Oman J Ophthalmol 2019;12:20-4. [doi: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_247_2017].Oman J Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb 27;14(1):64-65. doi: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_155_2019. eCollection 2021 Jan-Apr. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34084041 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[Optical coherence tomography predictive factors for idiopathic macular hole surgery outcome].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;49(9):807-11. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24330930 Chinese.
-
LONG-TERM OUTCOMES OF 23-GAUGE PARS PLANA VITRECTOMY WITH INTERNAL LIMITING MEMBRANE PEELING AND GAS TAMPONADE FOR MYOPIC TRACTION MACULOPATHY: A Prospective Study.Retina. 2015 Sep;35(9):1836-43. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000000554. Retina. 2015. PMID: 25946689
-
[Surgical Treatment of the Idiopathic Macular Hole by Means of 25-Gauge Pars Plana Vitrectomy with the Peeling of the Internal Limiting Membrane Assisted by Brilliant Blue and Gas Tamponade].Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2015 Jun;71(3):170-4. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 26201363 Czech.
-
Pre-operative predicting factor in visual outcome after macular hole surgery.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Jul-Aug;36(5):1053-1057. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.5.1995. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32704288 Free PMC article.
-
External limiting membrane aperture as a reliable and predictive prognostic factor in macular hole surgery.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 15:11206721251334161. doi: 10.1177/11206721251334161. Online ahead of print. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40232276
Cited by
-
Prognostic Factors for Visual Outcomes in Closed Idiopathic Macular Holes after Vitrectomy: Outcomes at 4 Years in a Monocentric Study.J Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr 23;2022:1553719. doi: 10.1155/2022/1553719. eCollection 2022. J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35529168 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the dilution method on the intraocular duration of C3F8 in vitrectomy for macular hole: a randomized clinical trial.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2024 Mar 4;87(2):e20220336. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.2022-0336. eCollection 2024. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2024. PMID: 38451686 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Incomplete fluid-air exchange technique for idiopathic macular hole surgery.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Oct 18;12(10):1582-1588. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2019.10.10. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31637194 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of horizontal and vertical posterior pole steepness on the dimensions of idiopathic macular hole.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025 Jun 23;11(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40942-025-00700-6. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025. PMID: 40551273 Free PMC article.
-
Frequently assessed and used prognostic factors for outcome after macular hole surgery: which is better?BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov 18;21(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02164-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34789189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bainbridge J, Herbert E, Gregor Z. Macular holes: Vitreoretinal relationships and surgical approaches. Eye (Lond) 2008;22:1301–9. - PubMed
-
- Williamson TH, Lee E. Idiopathic macular hole: Analysis of visual outcomes and the use of indocyanine green or brilliant blue for internal limiting membrane peel. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Tirelli F, Sasso P, Scupola A. Idiopathic macular hole: Post-operative morpho-functional assessment and prognostic factors for recovery of visual acuity. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2013;49:313–6. - PubMed
-
- Kelly NE, Wendel RT. Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Results of a pilot study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991;109:654–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous