Normal electro-oculography in a young Omani male with genetically confirmed best disease complicated by choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 30787533
- PMCID: PMC6380146
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_74_2018
Normal electro-oculography in a young Omani male with genetically confirmed best disease complicated by choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
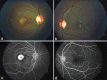
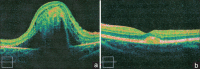
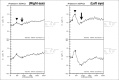
Best vitelliform macular dystrophy (VMD) is an autosomal dominant macular dystrophy caused by heterozygous mutations in the bestrophin1 gene. Patients with this condition typically have an abnormal electrooculogram. We report a case of a 16-year-old male who presented with gradual progressive vision loss in the right eye. Ophthalmic assessment included funduscopy, optical coherence tomography (OCT), fluorescein angiography, electro-oculography, electroretinography, and genetic testing. Visual acuity was 20/500 and 20/20 in the right and left eyes, respectively. Ophthalmoscopy revealed round yellow lesions in both foveae similar to what is typically seen in Best disease. A subretinal hemorrhage surrounding the right foveal lesion was also noted. OCT demonstrated an elevated neurosensory retina with a subretinal lesion in the right macula. Fluorescein angiography of the right eye confirmed the presence of choroidal neovascularization. Genetic analysis of VMD2/BEST1 sequences confirmed the diagnosis of Best disease. However, contrary to what was expected, the patient's electro-oculography was normal. The findings of this case support a small number of previous reports demonstrating cases of Best disease with normal electro-oculography. While an abnormal electro-oculography along with the typical features of Best disease confirms the diagnosis, a normal result may not exclude the diagnosis. Genetic testing is probably the most important test for establishing the diagnosis of Best disease.
Keywords: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor; best disease; choroidal neovascularization; electrooculography; vitelliform macular dystrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Petrukhin K, Koisti MJ, Bakall B, Li W, Xie G, Marknell T, et al. Identification of the gene responsible for best macular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1998;19:241–7. - PubMed
-
- Ryan SJ. Retina. London: Saunders; 2013. [Last accessed on 2016 Oct 03]. Available from: http:// www.clinicalkey.com/dura/browse/bookChapter/3-s2.0 -C20101695661 .
-
- Birndorf LA, Dawson WW. A normal electrooculogram in a patient with a typical vitelliform macular lesion. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973;12:830–3. - PubMed
-
- Krämer F, White K, Pauleikhoff D, Gehrig A, Passmore L, Rivera A, et al. Mutations in the VMD2 gene are associated with juvenile-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy (Best disease) and adult vitelliform macular dystrophy but not age-related macular degeneration. Eur J Hum Genet. 2000;8:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Pollack K, Kreuz FR, Pillunat LE. Best's disease with normal EOG. Case report of familial macular dystrophy. Ophthalmologe. 2005;102:891–4. - PubMed

