The benefit of taxane-based therapies over fluoropyrimidine plus platinum (FP) in the treatment of esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
- PMID: 30787595
- PMCID: PMC6368118
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S189514
The benefit of taxane-based therapies over fluoropyrimidine plus platinum (FP) in the treatment of esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
Abstract
Purpose: Fluoropyrimidine plus platinum (FP) is currently the standard treatment for esophageal cancer (EC). In recent years, taxane-based chemotherapy has also been used and has shown good efficacy in EC. This study aims to investigate the advantages of taxane-based over FP chemotherapy, as well as discuss its drawbacks, in the treatment of EC.
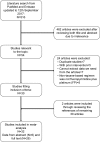
Patients and methods: A literature search was done for studies comparing clinical outcomes between taxane-based and FP chemotherapy in EC. Pooled analyses were performed to compare the efficacy and grade 3/4 adverse events in patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACRT), or definitive chemoradiotherapy (dCRT). Subgroup analyses were also conducted in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
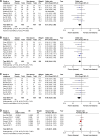
Results: Thirty-one studies with a total of 3,912 patients were included in the analysis. Better long-term survival was found in patients who received taxane-based NACT (progression-free survival (PFS): pooled HR=0.58, P=0.0008; and overall survival (OS): pooled HR=0.50, P<0.00001) and dCRT (PFS: pooled HR=0.75, P<0.0001). In NACRT, taxane-based treatment and FP showed similar efficacy. In ESCC patients, taxane-based treatment showed better OS (NACT: pooled HR=0.57, P=0.02; NACRT: pooled HR=0.51, P=0.03; and dCRT: pooled HR=0.73, P<0.0001) than FP chemotherapy. Furthermore, taxane-based therapy also showed a better short-term response (complete response (CR), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), or pathologic complete response (pCR). However, taxane-based therapy was significantly correlated with a higher incidence of grade 3/4 leukopenia, neutropenia, and diarrhea.
Conclusion: Compared to FP, taxane-based therapy produced better clinical response and outcomes in EC patients receiving NACT or dCRT, and in all types of therapy in patients with ESCC. Taxane-based treatment is associated with more frequent toxicity.
Keywords: chemotherapy; clinical cancer research; digestive cancer; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, et al. Global, regional, and National cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and Disability-Adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof M, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (cross): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(9):1090–1098. - PubMed
-
- Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(7):681–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

