D-Serine: Potential Therapeutic Agent and/or Biomarker in Schizophrenia and Depression?
- PMID: 30787885
- PMCID: PMC6372501
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00025
D-Serine: Potential Therapeutic Agent and/or Biomarker in Schizophrenia and Depression?
Abstract
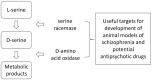
D-Serine is a potent co-agonist at the NMDA glutamate receptor and has been the object of many preclinical studies to ascertain the nature of its metabolism, its regional and cellular distribution in the brain, its physiological functions and its possible clinical relevance. The enzymes involved in its formation and catabolism are serine racemase (SR) and D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO), respectively, and manipulations of the activity of those enzymes have been useful in developing animal models of schizophrenia and in providing clues to the development of potential new antipsychotic strategies. Clinical studies have been conducted in schizophrenia patients to evaluate body fluid levels of D-serine and/or to use D-serine alone or in combination with antipsychotics to determine its effectiveness as a therapeutic agent. D-serine has also been used in combination with DAAO inhibitors in preclinical investigations, and interesting results have been obtained. Genetic studies and postmortem brain studies have also been conducted on D-serine and the enzymes involved in its metabolism. It is also of considerable interest that in recent years clinical and preclinical investigations have suggested that D-serine may also have antidepressant properties. Clinical studies have also shown that D-serine may be a biomarker for antidepressant response to ketamine. Relevant to both schizophrenia and depression, preclinical and clinical studies with D-serine indicate that it may be effective in reducing cognitive dysfunction.
Keywords: D-amino acid oxidase; D-amino acids; D-serine; depression; schizophrenia; serine racemase.
Figures

References
-
- Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Konno R, Niwa A, Yasumura Y, Oka T, et al. . Free D-serine, D-aspartate, and D-alanine in central nervous system and serum in mutant mice lacking D-amino acid oxidase. Neurosci Lett. (1993) 152:33–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

