Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Skews Human DC to Prime IL10-Producing T Cells Through TLR2/6/JNK Signaling and IL-10, IL-27, CD39, and IDO-1 Induction
- PMID: 30787928
- PMCID: PMC6373781
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00143
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Skews Human DC to Prime IL10-Producing T Cells Through TLR2/6/JNK Signaling and IL-10, IL-27, CD39, and IDO-1 Induction
Abstract
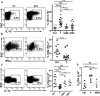
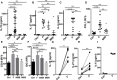
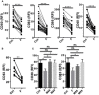
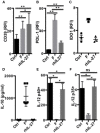
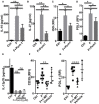
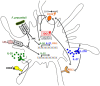
The human colonic mucosa contains regulatory type 1-like (Tr1-like, i.e., IL-10-secreting and Foxp3-negative) T cells specific for the gut Clostridium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (F. prausnitzii), which are both decreased in Crohn's disease patients. These data, together with the demonstration, in mice, that colonic regulatory T cells (Treg) induced by Clostridium bacteria are key players in colon homeostasis, support a similar role for F. prausnitzii-specific Treg in the human colon. Here we assessed the mechanisms whereby F. prausnitzii induces human colonic Treg. We demonstrated that F. prausnitzii, but not related Clostridia, skewed human dendritic cells to prime IL-10-secreting T cells. Accordingly, F. prausnitzii induced dendritic cells to express a unique array of potent Tr1/Treg polarizing molecules: IL-10, IL-27, CD39, IDO-1, and PDL-1 and, following TLR4 stimulation, inhibited their up-regulation of costimulation molecules as well as their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-12 (p35 and p40) and TNFα. We further showed that these potent tolerogenic effects relied on F. prausnitzii-induced TLR2/6 triggering, JNK signaling and CD39 ectonucleotidase activity, which was induced by IDO-1 and IL-27. These data, together with the presence of F. prausnitzii-specific Tr1-like Treg in the human colon, point out to dendritic cells polarization by F. prausnitzii as the first described cellular mechanism whereby the microbiota composition may affect human colon homeostasis. Identification of F. prausnitzii-induced mediators involved in Tr1-like Treg induction by dendritic cells opens therapeutic avenues for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Keywords: CD39; IDO-1; JNK; TLR2/6; Tr1-like Treg; colon homeostasis; dendritic cells; gut microbiota.
Figures

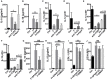
References
-
- Sarrabayrouse G, Bossard C, Chauvin JM, Jarry A, Meurette G, Quevrain E, et al. CD4CD8alphaalpha lymphocytes, a novel human regulatory T cell subset induced by colonic bacteria and deficient in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS Biol. (2014) 12:e1001833. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001833 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Godefroy E, Alameddine J, Montassier E, Mathe J, Desfrancois-Noel J, Marec N, et al. Expression of CCR6 and CXCR6 by Gut-derived CD4(+)/CD8alpha(+) T-regulatory cells which are decreased in blood samples from patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology (2018) 155:1205–17. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.078 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, Lakhdari O, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Gratadoux JJ, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2008) 105:16731–6. 10.1073/pnas.0804812105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

