Genomic Analysis of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Mycobacterium chimaera Infections, United States
- PMID: 30789131
- PMCID: PMC6390774
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2503.181282
Genomic Analysis of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Mycobacterium chimaera Infections, United States
Abstract
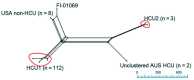
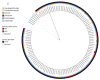
A surgical heater-cooler unit has been implicated as the source for Mycobacterium chimaera infections among cardiac surgery patients in several countries. We isolated M. chimaera from heater-cooler units and patient infections in the United States. Whole-genome sequencing corroborated a risk for these units acting as a reservoir for this pathogen.
Keywords: Mycobacterium chimaera; United States; bacteria; cardiac surgery; genomics; heater–cooler unit; nontuberculous mycobacteria; nosocomial infection; outbreak; tuberculosis and other mycobacteria.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

