Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase ameliorates hyperhomocysteinemia-induced hepatic steatosis by enhancing β-oxidation of fatty acid in mice
- PMID: 30789748
- PMCID: PMC6483021
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00148.2018
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase ameliorates hyperhomocysteinemia-induced hepatic steatosis by enhancing β-oxidation of fatty acid in mice
Abstract
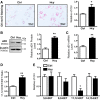
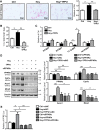
Hepatic steatosis is the beginning phase of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) is a significant risk factor. Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) hydrolyzes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and other epoxy fatty acids, attenuating their cardiovascular protective effects. However, the involvement of sEH in HHcy-induced hepatic steatosis is unknown. The current study aimed to explore the role of sEH in HHcy-induced lipid disorder. We fed 6-wk-old male mice a chow diet or 2% (wt/wt) high-metnionine diet for 8 wk to establish the HHcy model. A high level of homocysteine induced lipid accumulation in vivo and in vitro, which was concomitant with the increased activity and expression of sEH. Treatment with a highly selective specific sEH inhibitor (0.8 mg·kg-1·day-1 for the animal model and 1 μM for cells) prevented HHcy-induced lipid accumulation in vivo and in vitro. Inhibition of sEH activated the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α), as evidenced by elevated β-oxidation of fatty acids and the expression of PPAR-α target genes in HHcy-induced hepatic steatosis. In primary cultured hepatocytes, the effect of sEH inhibition on PPAR-α activation was further confirmed by a marked increase in PPAR-response element luciferase activity, which was reversed by knock down of PPAR-α. Of note, 11,12-EET ligand dependently activated PPAR-α. Thus increased sEH activity is a key determinant in the pathogenesis of HHcy-induced hepatic steatosis, and sEH inhibition could be an effective treatment for HHcy-induced hepatic steatosis. NEW & NOTEWORTHY In the current study, we demonstrated that upregulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is involved in the hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy)-caused hepatic steatosis in an HHcy mouse model and in murine primary hepatocytes. Improving hepatic steatosis in HHcy mice by pharmacological inhibition of sEH to activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α was ligand dependent, and sEH could be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Keywords: hepatocytes; hyperhomocysteinemia; proliferator-activated receptor-α; soluble epoxide hydrolase; β-oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acid attenuates hyperhomocysteinemia-induced hepatic steatosis by increasing hepatic LXA5 content].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2021 Aug 25;73(4):551-558. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34405211 Chinese.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/CD36 pathway to promote hepatic steatosis in mice.Hepatology. 2016 Jul;64(1):92-105. doi: 10.1002/hep.28518. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26928949
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates high-fat-diet-induced hepatic steatosis by reduced systemic inflammatory status in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039165. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22720061 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: gene structure, expression and deletion.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 20. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23701967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisomal beta-oxidation and steatohepatitis.Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21(1):43-55. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-12928. Semin Liver Dis. 2001. PMID: 11296696 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition in Liver Diseases: A Review of Current Research and Knowledge Gaps.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;9(6):124. doi: 10.3390/biology9060124. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the Effect of Sorafenib on Omega-6 and Omega-3 Epoxyeicosanoid Formation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 9;21(5):1875. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051875. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32182938 Free PMC article.
-
Zishen Qingre Tongluo Formula Improves Renal Fatty Acid Oxidation and Alleviated Fibrosis via the Regulation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 Signaling Pathway in Hyperuricemic Nephrology Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 13;2021:2793823. doi: 10.1155/2021/2793823. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34938805 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, TPPU, increases regulatory T cells pathway in an arthritis model.FASEB J. 2020 Jul;34(7):9074-9086. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000415R. Epub 2020 May 13. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32400048 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors from Chemical Synthesis and Natural Products.J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 14;64(1):184-215. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01507. Epub 2020 Dec 28. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33369424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

