Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15): A survival protein with therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases
- PMID: 30790643
- PMCID: PMC7196666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.02.008
Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15): A survival protein with therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases
Abstract
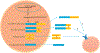
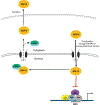
Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15), also known as NSAID activated gene-1 (NAG-1), is associated with a large number of biological processes and diseases, including cancer and obesity. GDF15 is synthesized as pro-GDF15, is dimerized, and is cleaved and secreted into the circulation as a mature dimer GDF15. Both the intracellular GDF15 and the circulating mature GDF15 are implicated in biological processes, such as energy homeostasis and body weight regulation. Although there have been many studies on GDF15, GFRAL, a member of the glial-derived neurotropic factor receptor α family, has only been recently identified as a receptor for mature GDF15. In this review, we focused on cancer and energy homeostasis along with obesity and body weight, and the effect of the identification of the GDF15 receptor in these investigations. In addition, the therapeutic potential of GDF15 as a pharmacological agent in obesity and other metabolic diseases was discussed.
Keywords: Aging; Appetite suppression; Cancer prevention; Energy metabolism; GFRAL receptor complex; Growth differentiation factor 15; Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug activated gene-1; Obesity; Survival.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Baek SJ, & Eling TE (2006). Changes in gene expression contribute to cancer prevention by COX inhibitors. Prog Lipid Res, 45, 1–16. - PubMed
-
- Baek SJ, Horowitz JM, & Eling TE (2001). Molecular cloning and characterization of human nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene promoter. Basal transcription is mediated by Sp1 and Sp3. J Biol Chem, 276, 33384–33392. - PubMed
-
- Baek SJ, Kim JS, Jackson FR, Eling TE, McEntee MF, & Lee SH (2004). Epicatechin gallate-induced expression of NAG-1 is associated with growth inhibition and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis, 25, 2425–2432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

