Dupilumab provides important clinical benefits to patients with atopic dermatitis who do not achieve clear or almost clear skin according to the Investigator's Global Assessment: a pooled analysis of data from two phase III trials
- PMID: 30791102
- PMCID: PMC6849829
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.17791
Dupilumab provides important clinical benefits to patients with atopic dermatitis who do not achieve clear or almost clear skin according to the Investigator's Global Assessment: a pooled analysis of data from two phase III trials
Abstract
Background: In the U.S.A., an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score of ≤ 1 (clear or almost clear skin) has been the standard measure in regulatory outcomes for registration clinical trials in atopic dermatitis (AD), including those supporting the recent approval of dupilumab.
Objectives: To evaluate the treatment effect of dupilumab in patients with IGA > 1 at the end of treatment, using other validated outcome measures for AD signs, symptoms and quality of life.
Methods: LIBERTY AD SOLO 1 and 2 were two 16-week, randomized, double-blind trials enrolling adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (IGA ≥ 3) inadequately controlled with topical treatment. We performed a post hoc analysis in patients receiving dupilumab 300 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) or placebo. Outcome measures in patients with IGA > 1 included Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), pruritus numerical rating scale (NRS), affected body surface area (BSA), Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). The trials were registered at ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02277743 and NCT02277769.
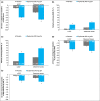
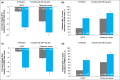
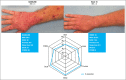
Results: At week 16, 278 of 449 dupilumab q2w-treated patients (median age 36·0 years) and 396 of 443 placebo-treated patients had IGA > 1. Among patients with IGA > 1 at week 16, dupilumab significantly improved several outcome measures compared with placebo: EASI (-48·9% vs. -11·3%, P < 0·001), pruritus NRS (-35·2% vs. -9·1%, P < 0·001), affected BSA (-23·1% vs. -4·5%, P < 0·001), POEM score ≥ 4-point improvement (57·4% vs. 21·0%, P < 0·001) and DLQI score ≥ 4-point improvement (59·3% vs. 24·4%, P < 0·001).
Conclusions: In patients with IGA > 1 at week 16, dupilumab induced statistically significant benefits in multiple validated outcome measures compared with placebo. The IGA ≤ 1 end point significantly underestimates clinically relevant dupilumab treatment effects.
© 2019 The Authors. British Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Figures
Comment in
-
Time to get rid of the Investigator's Global Assessment as the primary outcome for clinical trials in atopic dermatitis?Br J Dermatol. 2019 Jul;181(1):12-13. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18037. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31259405 No abstract available.
References
-
- Futamura M, Leshem YA, Thomas KS et al A systematic review of Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) in atopic dermatitis (AD) trials: many options, no standards. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016; 74:288–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

