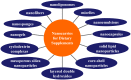
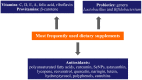
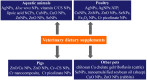
Potential of Nanomaterial Applications in Dietary Supplements and Foods for Special Medical Purposes
- PMID: 30791492
- PMCID: PMC6409737
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9020296
Potential of Nanomaterial Applications in Dietary Supplements and Foods for Special Medical Purposes
Abstract
Dietary supplements and foods for special medical purposes are special medical products classified according to the legal basis. They are regulated, for example, by the European Food Safety Authority and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, as well as by various national regulations issued most frequently by the Ministry of Health and/or the Ministry of Agriculture of particular countries around the world. They constitute a concentrated source of vitamins, minerals, polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants or other compounds with a nutritional or physiological effect contained in the food/feed, alone or in combination, intended for direct consumption in small measured amounts. As nanotechnology provides "a new dimension" accompanied with new or modified properties conferred to many current materials, it is widely used for the production of a new generation of drug formulations, and it is also used in the food industry and even in various types of nutritional supplements. These nanoformulations of supplements are being prepared especially with the purpose to improve bioavailability, protect active ingredients against degradation, or reduce side effects. This contribution comprehensively summarizes the current state of the research focused on nanoformulated human and veterinary dietary supplements, nutraceuticals, and functional foods for special medical purposes, their particular applications in various food products and drinks as well as the most important related guidelines, regulations and directives.
Keywords: bioactive agents; dietary supplements; encapsulation; feed; foodstuffs; nanoemulsions; nanoformulations; nanoparticles; nutraceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential of Nanonutraceuticals in Increasing Immunity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Nov 9;10(11):2224. doi: 10.3390/nano10112224. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
European regulations on nutraceuticals, dietary supplements and functional foods: a framework based on safety.Toxicology. 2006 Apr 3;221(1):59-74. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.12.022. Epub 2006 Feb 15. Toxicology. 2006. PMID: 16469424
-
Foodstuffs for particular nutritional purposes and dietary supplements in the legal-medical context.Wiad Lek. 2025;78(3):559-564. doi: 10.36740/WLek/202429. Wiad Lek. 2025. PMID: 40219882 Review.
-
[Food supplements : Legal requirements, borderline issues and other aspects].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2017 Mar;60(3):260-267. doi: 10.1007/s00103-016-2499-0. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2017. PMID: 28070624 Review. German.
-
Application of Nanoparticles in Human Nutrition: A Review.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 25;16(5):636. doi: 10.3390/nu16050636. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCN5 activation by free or encapsulated EGCG is required to render triple-negative breast cancer cell viability and tumor progression.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021 Apr;9(2):e00753. doi: 10.1002/prp2.753. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021. PMID: 33745223 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional significance of amino acids, vitamins and minerals as nutraceuticals in poultry production and health - a comprehensive review.Vet Q. 2020 Dec 7;41(1):1-29. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2020.1857887. Vet Q. 2020. PMID: 33250002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Nanostructures for Antimicrobial Therapy.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;15(7):2388. doi: 10.3390/ma15072388. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Strain-Probiotic-Loaded Nanoparticles Reduced Colon Inflammation and Orchestrated the Expressions of Tight Junction, NLRP3 Inflammasome and Caspase-1 Genes in DSS-Induced Colitis Model.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 31;14(6):1183. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061183. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745756 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophobic Homopolymer's Coil-Globule Transition and Adsorption onto a Hydrophobic Surface under Different Conditions.J Phys Chem B. 2023 Jun 29;127(25):5541-5552. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c00937. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Phys Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37334684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rao P.J., Naidu M.M. Nanoencapsulation of Bioactive Compounds for Nutraceutical Food. In: Ranjan S., Dasgupta N., Lichtfouse E., editors. Nanoscience in Food and Agriculture 2. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews. Volume 21. Springer; Cham, Germany: 2016. pp. 129–156.
-
- National Institutes of Health Dietary Supplements: Background Information. [(accessed on 20 November 2018)]; Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/DietarySupplements-HealthProfessional/
-
- European Commission Food Supplements. [(accessed on 20 November 2018)]; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/labelling_nutrition/supplements_en.
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration Dietary Supplements Guidance Documents & Regulatory Information. [(accessed on 20 November 2018)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryI....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials