Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in AFB smear-negative sputum specimens through MTB culture and GeneXpert® MTB/RIF assay
- PMID: 30791749
- PMCID: PMC6360468
- DOI: 10.1177/2058738419827174
Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in AFB smear-negative sputum specimens through MTB culture and GeneXpert® MTB/RIF assay
Abstract
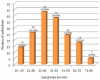
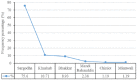
Tuberculosis (TB) is an important public health issue around the globe which is a chronic infectious disease and is still one of the major challenges for developing countries. The emergence of drug-resistant TB makes the condition worse and there is an urgent need of fast, highly sensitive diagnostic methods. This study was undertaken to evaluate the performance of GeneXpert® MTB/RIF assay and MTB culture for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) in sputum smear-negative pulmonary TB/drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) suspects. A total of 168 sputum smear-negative TB suspects were recruited for the study. Among the suspected TB cases, 52.98% were male and 47.02% were females with the mean age of 42 ± 17.6 years. All the sputum specimens collected from the study population were subjected to Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) smear microscopy, GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay, and MTB culture. The results revealed that, out of 168 acid-fast bacilli (AFB)/ZN smear microscopy-negative sputum specimens, 48 (28.57%) and 58 (34.52%) were detected MTB positive by GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay and MTB culture, respectively, while 120 (71.43%) and 110 (65.48%) suspected TB cases were confirmed negative by GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay and MTB culture, respectively. The study concluded that GeneXpert assay was found to be a rapid and accurate tool for MTB detection in smear-negative sputum specimens. GeneXpert has advantage over ZN smear microscopy and MTB culture as it detects MTB and rifampicin resistance simultaneously within 2 h with minimal biohazards.
Keywords: AFB-negative smears; GeneXpert assay; MTB culture; pulmonary tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of microscopic and xpert MTB diagnoses of presumptive mycobacteria tuberculosis infection: retrospective analysis of routine diagnosis at Cape Coast Teaching Hospital.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 2;24(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09566-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38956504 Free PMC article.
-
COMPARISON OF GeneXpert MTB/RIF ASSAY WITH CONVENTIONAL AFB SMEAR FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2017 Mar;48(2):313-21. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29641882
-
Evaluation of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay on extrapulmonary and respiratory samples other than sputum: a low burden country experience.Pathology. 2017 Jan;49(1):70-74. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Pathology. 2017. PMID: 27913043
-
Rapid and Simultaneous Tuberculosis and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance: A Review of Diagnostic Accuracy [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Dec 10. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2020 Dec 10. PMID: 33534447 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Effectiveness of GeneXpert® in the diagnosis of tuberculosis in people living with HIV/AIDS.Rev Saude Publica. 2021 Dec 17;55:89. doi: 10.11606/s1518-8787.2021055003125. eCollection 2021. Rev Saude Publica. 2021. PMID: 34932706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Assay, MTB Culture and Line Probe Assay for the Detection of MDR Tuberculosis in AFB Smear Negative Specimens.Diseases. 2022 Oct 6;10(4):82. doi: 10.3390/diseases10040082. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 36278581 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of microscopic and xpert MTB diagnoses of presumptive mycobacteria tuberculosis infection: retrospective analysis of routine diagnosis at Cape Coast Teaching Hospital.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 2;24(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09566-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38956504 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in BAL fluid samples from patients under clinical suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis: a tertiary care experience in a high-tuberculosis-burden area.J Bras Pneumol. 2021 May 17;47(2):e20200581. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20200581. eCollection 2021. J Bras Pneumol. 2021. PMID: 34008762 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-temporal analysis of pulmonary tuberculosis among students in the Zhejiang Province of China from 2007-2020.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 9;11:1114248. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1114248. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36844836 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-derived circulating cell-free DNA in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and persons with latent tuberculosis infection.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 24;16(6):e0253879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253879. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34166477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akram Y, Mahmood Z, Riaz M, et al. (2017) Biochemical profiling of tuberculosis patients co-infected with hepatitis C virus. European Journal of Inflammation 15(1): 42–45.
-
- World Health Organization (2017) Global Tuberculosis Report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization.
-
- Munir MK, Rehman S, Aasim M, et al. (2015) Comparison of Ziehl Neelsen microscopy with GeneXpert for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences 14(11): 56–60.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources