Reprint of: Voxel-Wise Longitudinal Parametric Response Mapping Analysis of Chest Computed Tomography in Smokers
- PMID: 30792137
- PMCID: PMC6704470
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2019.02.003
Reprint of: Voxel-Wise Longitudinal Parametric Response Mapping Analysis of Chest Computed Tomography in Smokers
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a heterogeneous disease characterized by small airway abnormality and emphysema. We hypothesized that a voxel-wise computed tomography analytic approach would identify patterns of disease progression in smokers.
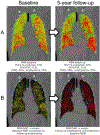
Materials and methods: We analyzed 725 smokers in spirometric GOLD stages 0-4 with two chest CTs 5 years apart. Baseline inspiration, follow-up inspiration and follow-up expiration images were spatially registered to baseline expiration so that each voxel had correspondences across all time points and respiratory phases. Voxel-wise Parametric Response Mapping (PRM) was then generated for the baseline and follow-up scans. PRM classifies lung as normal, functional small airway disease (PRMfSAD), and emphysema (PRMEMPH).
Results: Subjects with low baseline PRMfSAD and PRMEMPH predominantly had an increase in PRMfSAD on follow-up; those with higher baseline PRMfSAD and PRMEMPH mostly had increases in PRMEMPH. For GOLD 0 participants (n = 419), mean 5-year increases in PRMfSAD and PRMEMPH were 0.3% for both; for GOLD 1-4 participants (n = 306), they were 0.6% and 1.6%, respectively. Eighty GOLD 0 subjects (19.1%) had overall radiologic progression (30.0% to PRMfSAD, 52.5% to PRMEMPH, and 17.5% to both); 153 GOLD 1-4 subjects (50.0%) experienced progression (17.6% to PRMfSAD, 48.4% to PRMEMPH, and 34.0% to both). In a multivariable model, both baseline PRMfSAD and PRMEMPH were associated with development of PRMEMPH on follow-up, although this relationship was diminished at higher levels of baseline PRMEMPH.
Conclusion: A voxel-wise longitudinal PRM analytic approach can identify patterns of disease progression in smokers with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Computed tomography; Emphysema; Parametric Response Mapping; Small airway disease.
Copyright © 2018 The Association of University Radiologists. All rights reserved.
Figures

Republished from
-
Voxel-Wise Longitudinal Parametric Response Mapping Analysis of Chest Computed Tomography in Smokers.Acad Radiol. 2019 Feb;26(2):217-223. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.05.024. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Acad Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30055897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Labaki WW, Martinez CH, Martinez FJ, Galban CJ, Ross BD, Washko GR, Barr RG, Regan EA, Coxson HO, Hoffman EA, Newell JD Jr., Curran-Everett D, Hogg JC, Crapo JD, Lynch DA, Kazerooni EA, Han MK. The Role of Chest Computed Tomography in the Evaluation and Management of the Patient with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017; 196: 1372–1379. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahler DA, Wells CK. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest 1988; 93: 580–586. - PubMed
-
- Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, Littlejohns P. A self-complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. The St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992; 145: 1321–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- S10 OD018526/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900016C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX000911/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 HL122438/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900013C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL138188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007749/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900019C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900015C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900018C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK054759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900017C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900020C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

