Circadian clock protein Rev-erbα regulates neuroinflammation
- PMID: 30792350
- PMCID: PMC6421453
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1812405116
Circadian clock protein Rev-erbα regulates neuroinflammation
Abstract
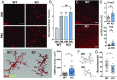
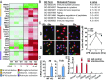
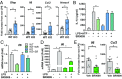
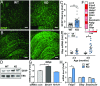
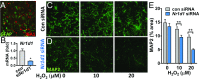
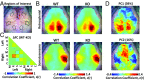
Circadian dysfunction is a common attribute of many neurodegenerative diseases, most of which are associated with neuroinflammation. Circadian rhythm dysfunction has been associated with inflammation in the periphery, but the role of the core clock in neuroinflammation remains poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that Rev-erbα, a nuclear receptor and circadian clock component, is a mediator of microglial activation and neuroinflammation. We observed time-of-day oscillation in microglial immunoreactivity in the hippocampus, which was disrupted in Rev-erbα-/- mice. Rev-erbα deletion caused spontaneous microglial activation in the hippocampus and increased expression of proinflammatory transcripts, as well as secondary astrogliosis. Transcriptomic analysis of hippocampus from Rev-erbα-/- mice revealed a predominant inflammatory phenotype and suggested dysregulated NF-κB signaling. Primary Rev-erbα-/- microglia exhibited proinflammatory phenotypes and increased basal NF-κB activation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that Rev-erbα physically interacts with the promoter regions of several NF-κB-related genes in primary microglia. Loss of Rev-erbα in primary astrocytes had no effect on basal activation but did potentiate the inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In vivo, Rev-erbα-/- mice exhibited enhanced hippocampal neuroinflammatory responses to peripheral LPS injection, while pharmacologic activation of Rev-erbs with the small molecule agonist SR9009 suppressed LPS-induced hippocampal neuroinflammation. Rev-erbα deletion influenced neuronal health, as conditioned media from Rev-erbα-deficient primary glial cultures exacerbated oxidative damage in cultured neurons. Rev-erbα-/- mice also exhibited significantly altered cortical resting-state functional connectivity, similar to that observed in neurodegenerative models. Our results reveal Rev-erbα as a pharmacologically accessible link between the circadian clock and neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Rev-erbα; circadian; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kondratov RV, Antoch MP. The clock proteins, aging, and tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:477–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

