BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer
- PMID: 30792387
- PMCID: PMC6384907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1407-6
BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer
Abstract
The BCl-2 family has long been identified for its role in apoptosis. Following the initial discovery of BCL-2 in the context of B-cell lymphoma in the 1980s, a number of homologous proteins have since been identified. The members of the Bcl-2 family are designated as such due to their BCL-2 homology (BH) domains and involvement in apoptosis regulation. The BH domains facilitate the family members' interactions with each other and can indicate pro- or anti-apoptotic function. Traditionally, these proteins are categorised into one of the three subfamilies; anti-apoptotic, BH3-only (pro-apoptotic), and pore-forming or 'executioner' (pro-apoptotic) proteins. Each of the BH3-only or anti-apoptotic proteins has a distinct pattern of activation, localisation and response to cell death or survival stimuli. All of these can vary across cell or stress types, or developmental stage, and this can cause the delineation of the roles of BCL-2 family members. Added to this complexity is the presence of relatively uncharacterised isoforms of many of the BCL-2 family members. There is a gap in our knowledge regarding the function of BCL-2 family isoforms. BH domain status is not always predictive or indicative of protein function, and several other important sequences, which can contribute to apoptotic activity have been identified. While therapeutic strategies targeting the BCL-2 family are constantly under development, it is imperative that we understand the molecules, which we are attempting to target. This review, discusses our current knowledge of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family isoforms. With significant improvements in the potential for splicing therapies, it is important that we begin to understand the distinctions of the BCL-2 family, not limited to just the mechanisms of apoptosis control, but in their roles outside of apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
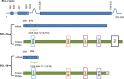
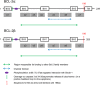
References
-
- Tsujimoto Y, et al. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984;226:1097–1099. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, et al. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985;228:1440–1443. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y. Stress-resistance conferred by high level of bcl-2 alpha protein in human B lymphoblastoid cell. Oncogene. 1989;4:1331–1336. - PubMed
-
- Yin XM, Oltvai ZN, Korsmeyer SJ. BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 1994;369:321–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

