The shape of human squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer
- PMID: 30792392
- PMCID: PMC6384927
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08866-y
The shape of human squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer
Abstract
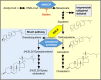
Squalene epoxidase (also known as squalene monooxygenase, EC 1.14.99.7) is a key rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. Anil Padyana and colleagues report the long awaited structure of human squalene epoxidase (SQLE). They solved the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human SQLE alone and in complex with two similar pharmacological inhibitors and elucidate their mechanism of action. SQLE is the target of fungicides and of increasing interest in human health and disease, particularly as a new anti-cancer target. Indeed, in a companion paper, Christopher Mahoney and colleagues performed an inhibitor screen with cancer cell lines and identified SQLE as an unique vulnerability in a subset of neuroendocrine tumours, where SQLE inhibition caused a toxic accumulation of the substrate squalene. The SQLE structure will facilitate the development of improved inhibitors. Here, we comment on these two studies in the wider context of the field and discuss possible future directions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and inhibition mechanism of the catalytic domain of human squalene epoxidase.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 9;10(1):97. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07928-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30626872 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical biology screen identifies a vulnerability of neuroendocrine cancer cells to SQLE inhibition.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 9;10(1):96. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07959-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30626880 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical toxicology profile of squalene epoxidase inhibitors.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 15;401:115103. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115103. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32522582
-
Multidimensional insights into squalene epoxidase drug development: in vitro mechanisms, in silico modeling, and in vivo implications.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025 Jun;29(6):385-403. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2025.2500420. Epub 2025 May 8. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025. PMID: 40304285 Review.
-
Advances in understanding the role of squalene epoxidase in cancer prognosis and resistance.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 27;52(1):162. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10276-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39869140 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol in colorectal cancer: an essential but tumorigenic precursor?Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 3;13:1276654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1276654. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38023258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol biogenesis is a PTEN-dependent actionable node for the treatment of endocrine therapy-refractory cancers.Cancer Sci. 2023 Nov;114(11):4365-4375. doi: 10.1111/cas.15960. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37706278 Free PMC article.
-
SQLE Knockdown inhibits bladder cancer progression by regulating the PTEN/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway through P53.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Sep 28;23(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02997-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37770925 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous toxic metabolites and implications in cancer therapy.Oncogene. 2020 Aug;39(35):5709-5720. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01395-9. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32709924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Microglial Metabolic Rewiring Synergizes with Immune-Checkpoint Blockade Therapy for Glioblastoma.Cancer Discov. 2023 Apr 3;13(4):974-1001. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0455. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 36649564 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

