Immunomodulatory Bonds of the Partnership between Dendritic Cells and T Cells
- PMID: 30792568
- PMCID: PMC6380512
- DOI: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018026790
Immunomodulatory Bonds of the Partnership between Dendritic Cells and T Cells
Abstract
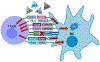
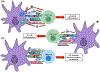
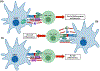
By acquiring, processing, and presenting both foreign and self-antigens, dendritic cells (DCs) initiate T cell activation that is shaped through the immunomodulatory functions of a variety of cell-membrane-bound molecules including BTLA-HVEM, CD40-CD40L, CTLA-4-CD80/CD86, CD70-CD27, ICOS-ICOS-L, OX40-OX40L, and PD-L1-PD-1, as well as several key cytokines and enzymes such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), retinaldehyde dehydrogenase (Raldh), and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Some of these distinct immunomodulatory signals are mediated by specific subsets of DCs, therefore contributing to the functional specialization of DCs in the priming and regulation of immune responses. In addition to responding to the DC-mediated signals, T cells can reciprocally modulate the immunomodulatory capacities of DCs, further refining immune responses. Here, we review recent studies, particularly in experimental mouse systems, that have delineated the integrated mechanisms of crucial immunomodulatory pathways that enable specific populations of DCs and T cells to work intimately together as single functional units that are indispensable for the maintenance of immune homeostasis.
Keywords: T cell; T cell differentiation; dendritic cell; effector T cell; immunoregulation; regulatory T cell.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
