Effect of music (Brahms lullaby) and non-nutritive sucking on heel lance in preterm infants: A randomized controlled crossover trial
- PMID: 30792607
- PMCID: PMC6376306
- DOI: 10.1093/pch/pxy072
Effect of music (Brahms lullaby) and non-nutritive sucking on heel lance in preterm infants: A randomized controlled crossover trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Effect of music (Brahms lullaby) and non-nutritive sucking on heel lance in preterm infants: A randomized controlled crossover trial.Paediatr Child Health. 2019 Feb;24(1):63. doi: 10.1093/pch/pxy163. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Paediatr Child Health. 2019. PMID: 30793710 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: This study examined a more effective pain management method, without sucrose, on heel lance in preterm infants using the Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP).
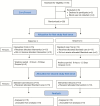
Design: In a nonblinded, randomized controlled, two-period, two-sequence crossover trial, 25 infants were randomly allocated to intervention (a Brahms lullaby with non-nutritive sucking, facilitated tucking and holding) or standard care (facilitated tucking and holding).
Setting: Local Perinatal Medical Centre's NICU in Japan, July 2014 until June 2015.
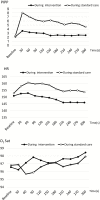
Outcome measures: The primary outcome variable was PIPP, and secondary outcomes were heart rate (HR), oxygen saturation, and abnormal HR (> baseline mean plus 2 SDs, or <120 minus 2 SDs).
Results: The infants were 33.8 weeks gestational age at birth, 1,983.7 g birth weight, and 32 to 35 weeks postconceptual age. At all 10 measurement points, constructed of every 30 seconds postheel lance, mean PIPP of infants during the intervention (3.6 to 2.4) was significantly lower than during the standard care (8.0 to 4.6) (range, P=0.0039 to P<0.0001). All PIPP reduction rates from the 30 seconds point were similar between the two groups. The HR of preterm infants at the 120 seconds points were significantly lower (P=0.0151), and the HRs of 6 points were considerably lower during the intervention than during the standard care (range, P≤0.0879 to P≥0.049). The abnormal HR total number was significantly lower during the intervention (2) than the standard care (23) (frequency ratio=0.087, P<0.0001).
Conclusion: This method demonstrated stronger analgesia, early pain relief, and maintenance of homeostasis on heel lance in preterm infants.
Keywords: Facilitated tucking; Heel lance; Music (Lullaby: Brahms); Non-nutritive sucking; Pain; Preterm infant.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson-Costello D. Is there evidence that long-term outcomes have improved with intensive care?Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2007;12(5):e344–54. - PubMed
-
- Carbajal R, Rousset A, Danan C, et al. Epidemiology and treatment of painful procedures in neonates in intensive care units. JAMA 2008;300(1):60–70. - PubMed
-
- Valeri BO, Holsti L, Linhares MB. Neonatal pain and developmental outcomes in children born preterm: A systematic review. Clin J Pain 2015;31(4):355–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical