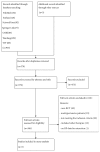
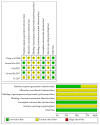
Corn Silk Tea for Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 30792743
- PMCID: PMC6354158
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2915498
Corn Silk Tea for Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Corn silk, a traditional Chinese medicine, has been found to exert an antihypertensive effect in clinical practice and trials. However, systematic review of current evidence on this topic was not available. Thus, this study aims to assess safety and efficacy of corn silk tea (CST) in improving clinical outcomes in patients with hypertension. A systematic literature search was conducted through popular electronic databases up to October 2018. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing CST plus conventional antihypertensive drugs with conventional antihypertensive drugs alone were included. The main outcome was total blood pressure lowering efficacy. The risk of bias assessment according to the Cochrane Handbook was used to evaluate the methodological quality of the included trials. Review Manager 5.3 software was used for data analyses. Five RCTs involving 567 participants were included. Due to the poor quality of methodologies of most trials, limited evidence showed that CST plus antihypertensive drugs might be more effective in lowering blood pressure compared with antihypertensive drugs alone (RR = 1.27; 95% CI: 1.17 to 1.38, P<0.00001; heterogeneity: P = 0.51, I 2 = 0%, fixed-effect model). However, there is no evidence that CST plus conventional antihypertensive drugs has less adverse events than conventional antihypertensive drugs.
Similar articles
-
Blood-Letting Therapy for Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Feb;25(2):139-146. doi: 10.1007/s11655-018-3009-2. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 29959751
-
Sodium Tanshinone II A Sulfonate for Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Mar;26(3):219-226. doi: 10.1007/s11655-018-2556-7. Epub 2018 May 11. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 29752695
-
Cochrane Review: Osmotic and stimulant laxatives for the management of childhood constipation (Review).Evid Based Child Health. 2013 Jan;8(1):57-109. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1893. Evid Based Child Health. 2013. PMID: 23878124 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine Xiao Yao San in hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytomedicine. 2019 Aug;61:152849. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152849. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31035044
-
Efficacy and safety of berberine for dyslipidaemias: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Phytomedicine. 2018 Nov 15;50:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.212. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466986
Cited by
-
Protection against Neurological Symptoms by Consuming Corn Silk Water Extract in Artery-Occluded Gerbils with Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Post-Stroke Hyperglycemia through the Gut-Brain Axis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 16;11(1):168. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010168. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052672 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of an Oral Solution Containing Five Herbal Extracts in the Treatment of Urolithiasis: A Randomized, Single-blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial.J Res Pharm Pract. 2024 Apr 30;12(3):96-103. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.jrpp_11_24. eCollection 2023 Jul-Sep. J Res Pharm Pract. 2024. PMID: 38716323 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential of Ma'aljobon, a whey product, in primary hypertension: A double-blind randomized controlled trial.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025 Jan-Feb;15(1):848-859. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2024.24921. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025. PMID: 40271499 Free PMC article.
-
An Umbrella Insight into the Phytochemistry Features and Biological Activities of Corn Silk: A Narrative Review.Molecules. 2024 Feb 18;29(4):891. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040891. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antihypertensive Effects of Corn Silk Extract and Its Novel Bioactive Constituent in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: The Involvement of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition.Molecules. 2019 May 16;24(10):1886. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101886. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31100914 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources