Facility Layout Planning with SHELL and Fuzzy AHP Method Based on Human Reliability for Operating Theatre
- PMID: 30792832
- PMCID: PMC6354165
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8563528
Facility Layout Planning with SHELL and Fuzzy AHP Method Based on Human Reliability for Operating Theatre
Abstract
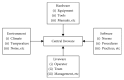
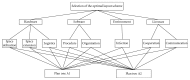
A well-design facility layout planning refers to the reduction of the operation cost in the manufacturing and service industry. This work consists of reliability analysis of facility layout for an operating theatre; it aims at proposing a new evaluation approach, which integrated the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and human reliability tool, for optimization of facility layout design with safety and human factors in an operating theatre. Firstly, the systematic layout planning is used to design the layout schemes on the basis of field investigations. Then, the criteria system is proposed based on human reliability analysis from four perspectives: software, hardware, environment, and liveware. Finally, the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process, a fuzzy extension of the multicriteria decision-making technique analytic hierarchy process, is used to compare these layout schemes based on the criteria system. The results that are obtained reveal interesting properties of facility layout planning in hospitals. It reveals that decision in selecting a suitable layout must meet not only the strategies and goals of the system but also meet the safety, security, and reliability of the system.
Figures




References
-
- Podtschaske B. Berlin, Germany: Technischen Universität Berlin, der Fakultät VII–Wirschaft und Management; 2012. Analyse and gestaltung komplexer arbeitssysteme am beispiel der Patientenversorgung. Dissertation.
-
- Shortell S. M., Kaluzny A. D. Health Care Management: Organization Design and Behavior. 4th. New York, NY, USA: Delmar; 2000.
-
- Heine R. P., Maddox E. N. Hospital Management Reform: A Step of Healthcare Reform. 2013. http://www.aabri.com/manuscripts/10443.pdf.
-
- Gul M., Guneri A. F. A computer simulation model to reduce patient length of stay and to improve resource utilization rate in an emergency department service system. International Journal of Industrial Engineering–Theory Applications and Practice. 2012;19(5):221–231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

