Sculpting stable structures in pure liquids
- PMID: 30793033
- PMCID: PMC6377271
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4283
Sculpting stable structures in pure liquids
Abstract
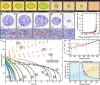
Pure liquids in thermodynamic equilibrium are structurally homogeneous. In liquid crystals, flow and light pulses are used to create reconfigurable domains with polar order. Moreover, through careful engineering of concerted microfluidic flows and localized optothermal fields, it is possible to achieve complete control over the nucleation, growth, and shape of such domains. Experiments, theory, and simulations indicate that the resulting structures can be stabilized indefinitely, provided the liquids are maintained in a controlled nonequilibrium state. The resulting sculpted liquids could find applications in microfluidic devices for selective encapsulation of solutes and particles into optically active compartments that interact with external stimuli.
Figures


References
-
- P. M. Chaikin, T. C. Lubensky, Principles of Condensed Matter Physics (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1995).
-
- Fert A., Reyren N., Cros V., Magnetic skyrmions: Advances in physics and potential applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17031 (2017).
-
- Hellman F., Hoffmann A., Tserkovnyak Y., Beach G. S. D., Fullerton E. E., Leighton C., MacDonald A. H., Ralph D. C., Arena D. A., Dürr H. A., Fischer P., Grollier J., Heremans J. P., Jungwirth T., Kimel A. V., Koopmans B., Krivorotov I. N., May S. J., Petford-Long A. K., Rondinelli J. M., Samarth N., Schuller I. K., Slavin A. N., Stiles M. D., Tchernyshyov O., Thiaville A., Zink B. L., Interface-induced phenomena in magnetism. Rev. Mod. Phys. 89, 025006 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- A. Onuki, Phase Transition Dynamics (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2004).
-
- P. G. Debenedetti, Metastable Liquids (Princeton Univ. Press, 1996).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

