Effects of vatinoxan on cardiorespiratory function and gastrointestinal motility during constant-rate medetomidine infusion in standing horses
- PMID: 30793362
- PMCID: PMC6767159
- DOI: 10.1111/evj.13085
Effects of vatinoxan on cardiorespiratory function and gastrointestinal motility during constant-rate medetomidine infusion in standing horses
Abstract
Background: Medetomidine suppresses cardiovascular function and reduces gastrointestinal motility in horses mainly through peripheral α2 -adrenoceptors. Vatinoxan, a peripheral α2 -antagonist, has been shown experimentally to alleviate the adverse effects of some α2 -agonists in horses. However, vatinoxan has not been investigated during constant-rate infusion (CRI) of medetomidine in standing horses.
Objectives: To evaluate effects of vatinoxan on cardiovascular function, gastrointestinal motility and on sedation level during CRI of medetomidine.
Study design: Experimental, randomised, blinded, cross-over study.
Methods: Six healthy horses were given medetomidine hydrochloride, 7 μg/kg i.v., without (MED) and with (MED+V) vatinoxan hydrochloride, 140 μg/kg i.v., followed by CRI of medetomidine at 3.5 μg/kg/h for 60 min. Cardiorespiratory variables were recorded and borborygmi and sedation levels were scored for 120 min. Plasma drug concentrations were measured. The data were analysed using repeated measures ANCOVA and paired t-tests as appropriate.
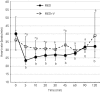
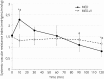
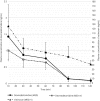
Results: Initially heart rate (HR) was significantly lower and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) significantly higher with MED compared with MED+V. For example at 10 min HR (mean ± s.d.) was 26 ± 2 and 31 ± 5 beats/minute (P = 0.04) and MAP 129 ± 15 and 103 ± 13 mmHg (P<0.001) respectively. At 10 min, cardiac index was lower (P = 0.02) and systemic vascular resistance higher (P = 0.001) with MED than with MED+V. Borborygmi were reduced after MED; this effect was attenuated by vatinoxan (P<0.001). All horses were sedated with medetomidine, but the mean sedation scores were reduced with MED+V until 20 min (6.8 ± 0.8 and 4.5 ± 1.5 with MED and MED+V, respectively, at 10 min, P = 0.001). Plasma concentration of dexmedetomidine was significantly lower in the presence of vatinoxan (P = 0.01).
Main limitations: Experimental study with healthy, unstimulated animals.
Conclusions: Vatinoxan administered i.v. with a loading dose of medetomidine improved cardiovascular function and gastrointestinal motility during medetomidine CRI in healthy horses. Sedation was slightly yet significantly reduced during the first 20 min.. The Summary is available in Portuguese - see Supporting Information.
Keywords: MK-467; horse; medetomidine; sedation; vatinoxan; α2-antagonist.
© 2019 The Authors. Equine Veterinary Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of EVJ Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Pertovaara, A. (1993) Antinociception induced by α2‐adrenoceptor agonists, with special emphasis on medetomidine studies. Prog. Neurobiol. 40, 691‐709. - PubMed
-
- Bettschart‐Wolfensberger, R. , Clarke, K.W. , Vainio, O. , Aliabadi, F. and Demuth, D. (1999) Pharmacokinetics of medetomidine in ponies and elaboration of a medetomidine infusion regime which provides a constant level of sedation. Res. Vet. Sci. 67, 41‐46. - PubMed
-
- Ranheim, B. , Risberg, A.I. , Spadavecchia, C. , Landsem, R. and Haga, H.A. (2015) The pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine administered as a constant rate infusion in horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 38, 93‐96. - PubMed
-
- Bettschart‐Wolfensberger, R. , Bettschart, R.W. , Vainio, O. , Marlin, D. and Clarke, K.W. (1999) Cardiopulmonary effects of a two hour medetomidine infusion and its antagonism by atipamezole in horses and ponies. Vet Anaesth. Analg. 26, 8‐12.
-
- Flacke, J.W. , Flacke, W.E. , Bloor, B.C. and McIntee, D.F. (1990) Hemodynamic effects of dexmedetomidine, an α2‐adrenergic agonist, in autonomically denervated dogs. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 16, 616‐623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

