Lower rates of cardiovascular events and mortality associated with liraglutide use in patients treated with basal insulin: A DEVOTE subanalysis (DEVOTE 10)
- PMID: 30793465
- PMCID: PMC6504564
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13677
Lower rates of cardiovascular events and mortality associated with liraglutide use in patients treated with basal insulin: A DEVOTE subanalysis (DEVOTE 10)
Abstract
Aim: To compare the associations between concomitant liraglutide use versus no liraglutide use and the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and all-cause mortality among patients receiving basal insulin (either insulin degludec [degludec] or insulin glargine 100 units/mL [glargine U100]) in the Trial Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Insulin Degludec versus Insulin Glargine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes at High Risk of Cardiovascular Events (DEVOTE).
Materials and methods: Patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk were randomized 1:1 to degludec or glargine U100. Hazard ratios for MACE/mortality were calculated using a Cox regression model adjusted for treatment and time-varying liraglutide use at any time during the trial, without interaction. Sensitivity analyses were adjusted for baseline covariates including, but not limited to, age, sex, smoking and prior cardiovascular disease.
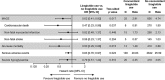
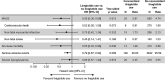
Results: At baseline, 436/7637 (5.7%) patients were treated with liraglutide; after baseline, 187/7637 (2.4%) started and 210/7637 (2.7%) stopped liraglutide. Mean liraglutide exposure from randomization was 530.2 days. Liraglutide use versus no liraglutide use was associated with significantly lower hazard rates for MACE [0.62 (0.41; 0.92)95%CI ] and all-cause mortality [0.50 (0.29; 0.88)95%CI ]. There was no significant difference in the rate of severe hypoglycaemia with versus without liraglutide use. Multiple sensitivity analyses yielded similar results.
Conclusions: Use of liraglutide was associated with significantly lower risk of MACE and death in patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk using basal insulin.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; hypoglycaemia; insulin therapy; liraglutide; randomized trial; type 2 diabetes.
© 2019 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Data sharing statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Figures
References
-
- Diabetes mellitus: a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. A joint editorial statement by the American Diabetes Association; The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; The Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International; The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; and The American Heart Association. Circulation. 1999;100:1132‐1133. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Diabetes+mellitus:+a+major+ris... - PubMed
-
- FDA . Guidance for industry. Diabetes mellitus — evaluating cardiovascular risk in new antidiabetic therapies to treat type 2 diabetes. December 2008. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformat.... Accessed March 2019.
-
- Gerstein HC, Bosch J, Dagenais GR, et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:319‐328. - PubMed

