Inhibition of P53/miR-34a improves diabetic endothelial dysfunction via activation of SIRT1
- PMID: 30793480
- PMCID: PMC6484332
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14253
Inhibition of P53/miR-34a improves diabetic endothelial dysfunction via activation of SIRT1
Abstract
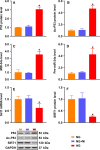
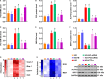
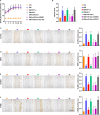
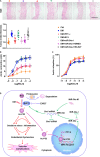
Endothelial dysfunction contributes to diabetic macrovascular complications, resulting in high mortality. Recent findings demonstrate a pathogenic role of P53 in endothelial dysfunction, encouraging the investigation of the effect of P53 inhibition on diabetic endothelial dysfunction. Thus, high glucose (HG)-treated endothelial cells (ECs) were subjected to pifithrin-α (PFT-α)-a specific inhibitor of P53, or P53-small interfering RNA (siRNA), both of which attenuated the HG-induced endothelial inflammation and oxidative stress. Moreover, inhibition of P53 by PFT-α or P53-siRNA prohibited P53 acetylation, decreased microRNA-34a (miR-34a) level, leading to a dramatic increase in sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) protein level. Interestingly, the miR-34a inhibitor (miR-34a-I) and PFT-α increased SIRT1 protein level and alleviated the HG-induced endothelial inflammation and oxidative stress to a similar extent; however, these effects of PFT-α were completely abrogated by the miR-34a mimic. In addition, SIRT1 inhibition by EX-527 or Sirt1-siRNA completely abolished miR-34a-I's protection against HG-induced endothelial inflammation and oxidative stress. Furthermore, in the aortas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, both PFT-α and miR-34a-I rescued the inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction caused by hyperglycaemia. Hence, the present study has uncovered a P53/miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway that leads to endothelial dysfunction, suggesting that P53/miR-34a inhibition could be a viable strategy in the management of diabetic macrovascular diseases.
Keywords: P53; aorta; diabetes; endothelial dysfunction; miR-34a.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
P66Shc-Induced MicroRNA-34a Causes Diabetic Endothelial Dysfunction by Downregulating Sirtuin1.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Dec;36(12):2394-2403. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308321. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27789474 Free PMC article.
-
SRT2104 attenuates diabetes-induced aortic endothelial dysfunction via inhibition of P53.J Endocrinol. 2018 Apr;237(1):1-14. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0672. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29371235
-
Carbon monoxide protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating the miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1852(7):1550-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25916635
-
MicroRNA-34a: the bad guy in age-related vascular diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7355-7378. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03979-4. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34698884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 pathway in Parkinson's disease: a faraway snapshot but so close.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Feb;31(1):37-56. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01125-5. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36580159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective role of NRF2 in macrovascular complications of diabetes.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Aug;24(16):8903-8917. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15583. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32628815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperglycemia Changes Expression of Key Adipogenesis Markers (C/EBPα and PPARᵞ)and Morphology of Differentiating Human Visceral Adipocytes.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 8;11(8):1835. doi: 10.3390/nu11081835. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31398873 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role of kallikrein-related peptidase 8 in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiac fibrosis.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 20;11(9):4207-4231. doi: 10.7150/thno.48530. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754057 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and MicroRNAs in Endothelial Cells under Metabolic Disorders.Cells. 2023 May 8;12(9):1341. doi: 10.3390/cells12091341. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR34a-5p impedes CLOCK expression in chronodisruptive C57BL/6J mice and potentiates pro-atherogenic manifestations.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 10;18(8):e0283591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283591. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37561715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forbes JM, Yee LT, Thallas V, et al. Advanced glycation end product interventions reduce diabetes‐accelerated atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 2004;53:1813‐1823. - PubMed
-
- King GL, Wakasaki H. Theoretical mechanisms by which hyperglycemia and insulin resistance could cause cardiovascular diseases in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(Suppl 3):C31‐C37. - PubMed
-
- Wu H, Wu J, Zhou S, et al. SRT2104 attenuates diabetes‐induced aortic endothelial dysfunction via inhibition of P53. J Endocrinol. 2018;237:3538‐14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

