MARCH1 encourages tumour progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of PI3K-AKT-β-catenin pathways
- PMID: 30793486
- PMCID: PMC6484336
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14235
MARCH1 encourages tumour progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of PI3K-AKT-β-catenin pathways
Abstract
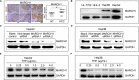
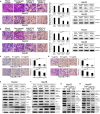
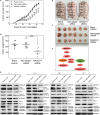
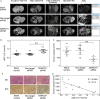
Membrane-associated RING-CH-1 (MARCH1) is a membrane-anchored E3 ubiquitin ligase that is involved in a variety of cellular processes. MARCH1 was aberrantly expressed as a tumour promoter in ovarian cancer, but the signalling about the molecular mechanism has not yet been fully illuminated. Here, we first determined that MARCH1 was obviously highly expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma samples and cells. In addition, our findings demonstrated that the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma were suppressed, but the apoptosis was increased, as a result of MARCH1 knockdown by either siRNA targeting MARCH1 or pirarubicin treatment. Conversely, the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma were obviously accelerated, and the apoptosis was decreased, by transfecting the MARCH1 plasmid to make MARCH1 overexpressed. Moreover, in vivo, the results exhibited a significant inhibition of the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice, which were given an intra-tumour injection of siRNA targeting MARCH1. Furthermore, our study concluded that MARCH1 functions as a tumour promoter, and its role was up-regulated the PI3K-AKT-β-catenin pathways both in vitro and in vivo. In summary, our work determined that MARCH1 has an important role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and may be used as a novel potential molecular therapeutic target in the future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: Invasion; MARCH1; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; migration; nude mouse model; pathways; pirarubicin; proliferation.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301‐1314. - PubMed
-
- Feng F, Jiang Q, Jia H, et al. Which is the best combination of TACE and Sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treatment? A systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Pharmacol Res. 2018;135:89‐101. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R, de Baere T, Soulen MC, Rilling WS, Geschwind JF. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology. 2016;64:106‐116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

