Acid-sensing ion channel 1a is involved in ischaemia/reperfusion induced kidney injury by increasing renal epithelia cell apoptosis
- PMID: 30793492
- PMCID: PMC6484315
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14238
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a is involved in ischaemia/reperfusion induced kidney injury by increasing renal epithelia cell apoptosis
Abstract
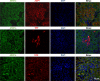
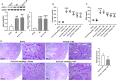
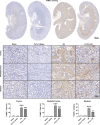
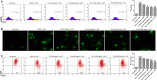
Acidic microenvironment is commonly observed in ischaemic tissue. In the kidney, extracellular pH dropped from 7.4 to 6.5 within 10 minutes initiation of ischaemia. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) can be activated by pH drops from 7.4 to 7.0 or lower and permeates to Ca2+ entrance. Thus, activation of ASIC1a can mediate the intracellular Ca2+ accumulation and play crucial roles in apoptosis of cells. However, the role of ASICs in renal ischaemic injury is unclear. The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that ischaemia increases renal epithelia cell apoptosis through ASIC1a-mediated calcium entry. The results show that ASIC1a distributed in the proximal tubule with higher level in the renal tubule ischaemic injury both in vivo and in vitro. In vivo, Injection of ASIC1a inhibitor PcTx-1 previous to ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) operation attenuated renal ischaemic injury. In vitro, HK-2 cells were pre-treated with PcTx-1 before hypoxia, the intracellular concentration of Ca2+ , mitochondrial transmembrane potential (∆ψm) and apoptosis was measured. Blocking ASIC1a attenuated I/R induced Ca2+ overflow, loss of ∆ψm and apoptosis in HK-2 cells. The results revealed that ASIC1a localized in the proximal tubular and contributed to I/R induced kidney injury. Consequently, targeting the ASIC1a may prove to be a novel strategy for AKI patients.
Keywords: acid-sensing ion channels; apoptosis; calcium; ischaemia/reperfusion injury; kidney; mitochondrial transmembrane potential.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Figures

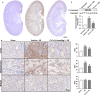
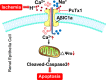
Similar articles
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Jul;101(7):877-890. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02330-7. Epub 2023 May 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37246982 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a mediates acid-induced increases in intracellular calcium in rat articular chondrocytes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jul;340(1-2):153-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0412-y. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20179994
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a is involved in retinal ganglion cell death induced by hypoxia.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3300-8. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22194656 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channels.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):271-84. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.026. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17113616 Review.
-
Acid-sensing ion channels under hypoxia.Channels (Austin). 2013 Jul-Aug;7(4):231-7. doi: 10.4161/chan.25223. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Channels (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23764948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ASIC1α up-regulates MMP-2/9 expression to enhance mobility and proliferation of liver cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 16;22(1):778. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09874-w. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35840921 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels: Expression and Function in Resident and Infiltrating Immune Cells in the Central Nervous System.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Sep 17;15:738043. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.738043. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34602982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intelligent podocyte: sensing and responding to a complex microenvironment.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jul;21(7):503-516. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00965-y. Epub 2025 May 8. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40341763 Review.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels and Mechanosensation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 1;22(9):4810. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094810. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34062742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel 2 promotes renal fibrosis by inducing cell-cycle arrest.iScience. 2022 Nov 17;25(12):105620. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105620. eCollection 2022 Dec 22. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36465115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prathapasinghe GA, Siow YL, Xu Z. Inhibition of cystathionine‐beta‐synthase activity during renal ischemia‐reperfusion: role of pH and nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295:F912–F922. - PubMed
-
- Sola A, Palacios L, Lopez‐Marti J, et al. Multiparametric monitoring of ischemia‐reperfusion in rat kidney: effect of ischemic preconditioning. Transplantation. 2003;75:744‐749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

