Introduction and Evaluation of an Electronic Tool for Improved Data Quality and Data Use during Malaria Case Management Supportive Supervision
- PMID: 30793695
- PMCID: PMC6447118
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0366
Introduction and Evaluation of an Electronic Tool for Improved Data Quality and Data Use during Malaria Case Management Supportive Supervision
Abstract
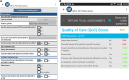
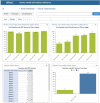
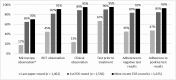
Although on-site supervision programs are implemented in many countries to assess and improve the quality of care, few publications have described the use of electronic tools during health facility supervision. The President's Malaria Initiative-funded MalariaCare project developed the MalariaCare Electronic Data System (EDS), a custom-built, open-source, Java-based, Android application that links to District Health Information Software 2, for data storage and visualization. The EDS was used during supervision visits at 4,951 health facilities across seven countries in Africa. The introduction of the EDS led to dramatic improvements in both completeness and timeliness of data on the quality of care provided for febrile patients. The EDS improved data completeness by 47 percentage points (42-89%) on average when compared with paper-based data collection. The average time from data submission to a final data analysis product dropped from over 5 months to 1 month. With more complete and timely data available, the Ministry of Health and the National Malaria Control Program (NMCP) staff could more effectively plan corrective actions and promptly allocate resources, ultimately leading to several improvements in the quality of malaria case management. Although government staff used supervision data during MalariaCare-supported lessons learned workshops to develop plans that led to improvements in quality of care, data use outside of these workshops has been limited. Additional efforts are required to institutionalize the use of supervision data within ministries of health and NMCPs.
Figures

References
-
- Amoakoh-Coleman M, Borgstein AB, Sondaal SF, Grobbee DE, Miltenburg AS, Verwijs M, Ansah EK, Browne JL, Klipstein-Grobusch K, 2016. Effectiveness of mHealth interventions targeting health care workers to improve pregnancy outcomes in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. J Med Internet Res 18: e226. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

