Cachexia and advanced dementia
- PMID: 30794350
- PMCID: PMC6463474
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12380
Cachexia and advanced dementia
Abstract
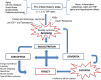
Cachexia is a complex metabolic process that is associated with several end-stage organ diseases. It is known to be also associated with advanced dementia, although the pathophysiologic mechanisms are still largely unknown. The present narrative review is aimed at presenting recent insights concerning the pathophysiology of weight loss and wasting syndrome in dementia, the putative mechanisms involved in the dysregulation of energy balance, and the interplay among the chronic clinical conditions of sarcopenia, malnutrition, and frailty in the elderly. We discuss the clinical implications of these new insights, with particular attention to the challenging question of nutritional needs in advanced dementia and the utility of tube feeding in order to optimize the management of end-stage dementia.
Keywords: Advanced dementia; Cachexia; Failure to thrive; Frailty; Sarcopenia; Supportive care.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Morley JE. Undernutrition: a major problem in nursing homes. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2011;12:243–246. - PubMed
-
- Muscaritoli M, Anker SD, Argilés J, Aversa Z, Bauer JM, Biolo G, et al. Consensus definition of sarcopenia, cachexia and pre‐cachexia: joint document elaborated by Special Interest Groups (SIG) “cachexia–anorexia in chronic wasting diseases” and “nutrition in geriatrics”. Clin Nutr 2010. Apr;29:154–159. - PubMed
-
- Conte C, Cascino A, Bartali B, Donini L, Rossi‐Fanelli F, Laviano A. Anorexia of aging. Curr Nutr Food Sci 2009;5:9–12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical