Secreted frizzled related protein is a target of PaxB and plays a role in aquiferous system development in the freshwater sponge, Ephydatia muelleri
- PMID: 30794564
- PMCID: PMC6386478
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212005
Secreted frizzled related protein is a target of PaxB and plays a role in aquiferous system development in the freshwater sponge, Ephydatia muelleri
Abstract
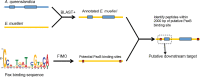
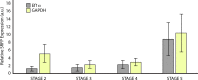
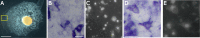
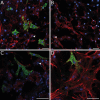
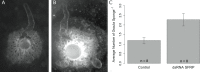
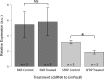
Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling, as well as the Pax/Six gene network, are involved in patterning the freshwater sponge aquiferous system. Using computational approaches to identify transcription factor binding motifs in a freshwater sponge genome, we located putative PaxB binding sites near a Secreted Frizzled Related Protein (SFRP) gene in Ephydatia muelleri. EmSFRP is expressed throughout development, but with highest levels in juvenile sponges. In situ hybridization and antibody staining show EmSFRP expression throughout the pinacoderm and choanoderm in a subpopulation of amoeboid cells that may be differentiating archeocytes. Knockdown of EmSFRP leads to ectopic oscula formation during development, suggesting that EmSFRP acts as an antagonist of Wnt signaling in E. muelleri. Our findings support a hypothesis that regulation of the Wnt pathway by the Pax/Six network as well as the role of Wnt signaling in body plan morphogenesis was established before sponges diverged from the rest of the metazoans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

