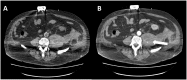
Spontaneous ilio-psoas hematomas complicating intensive care unit hospitalizations
- PMID: 30794573
- PMCID: PMC6386274
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211680
Spontaneous ilio-psoas hematomas complicating intensive care unit hospitalizations
Abstract
Background: Ilio-psoas hematoma is a potentially lethal condition that can arise during hospital stay. However, neither the incidence nor the prognosis of patients whose stay in intensive care units (ICU) is complicated by a iatrogenic ilio-psoas hematoma is known.
Methods: A bicentric retrospective study was conducted to compile the patients who developed an ilio-psoas hematoma while they were hospitalized in ICU between January 2009 and December 2016. Their biometric characteristics, pre-existing conditions, the circumstances in which the hematoma was diagnosed, the treatments they received and their prognosis were recorded.
Results: Forty patients were diagnosed with an ilio-psoas hematoma during their ICU stay. The incidence of this complication was 3.8 cases for 1000 admissions, taking into account only patients who stayed more than three days in ICU. The median age of patients was 74 years old and the median time between admission and the diagnosis of ilio-psoas hematoma was 12.6 days. A large proportion of them was obese (42.5%) and/or under dialysis (50%) prior to developing their hematoma. Ninety-five percent of the patients had heparin at prophylactic or therapeutic doses. Only 10% of them were above the therapeutic range of anticoagulation. The ICU mortality rate was of 50% following this complication (versus a general mortality rate of 22% for the patients without IPH over the same period of time). Patients with IPH that were complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulopathy had a significantly higher mortality rate than those with IPH and no disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (OR 6.91, 95% CI [1.28; 58.8], p = 0.04).
Conclusion: Age, anticoagulation, a high body mass index and dialysis seem to be risk factors of developing an ilio-psoas hematoma in ICU. Iatrogenic ilio-psoas hematomas complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulopathies are more at risk of leading to death. It is noteworthy that activated partial thromboplastin time above the therapeutic range was not a good predictor of developing a hematoma for patients who received unfractioned heparin therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Goldhill DR, Sumner A. Outcome of intensive care patients in a group of British intensive care units. Crit Care Med. 1998. August;26(8):1337–45. - PubMed
-
- Sakr Y, Moreira CL, Rhodes A, Ferguson ND, Kleinpell R, Pickkers P, et al. The impact of hospital and ICU organizational factors on outcome in critically ill patients: results from the Extended Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care study. Crit Care Med. 2015. March;43(3):519–26. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000754 - DOI - PubMed
-
- González C, Penado S, Llata L, Valero C, Riancho JA. The clinical spectrum of retroperitoneal hematoma in anticoagulated patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003. July;82(4):257–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources