HEWL interacts with dissipated oleic acid micelles, and decreases oleic acid cytotoxicity
- PMID: 30794655
- PMCID: PMC6386356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212648
HEWL interacts with dissipated oleic acid micelles, and decreases oleic acid cytotoxicity
Erratum in
-
Correction: HEWL interacts with dissipated oleic acid micelles, and decreases oleic acid cytotoxicity.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 22;14(8):e0221704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221704. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31437263 Free PMC article.
Abstract
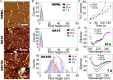
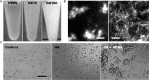
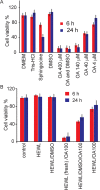
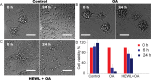
Senile plaques are well-known hallmarks of Alzheimer's Diseases (AD). However, drugs targeting tangles of the protein tau and plaques of β-amyloid have no significant effect on disease progression, and the studies on the underlying mechanism of AD remain in high demand. Growing evidence supports the protective role of senile plaques in local inflammation driven by S100A9. We herein demonstrate that oleic acid (OA) micelles interact with hen egg white lysozyme (HEWL) and promote its amyloid formation. Consequently, SH-SY5Y cell line and mouse neural stem cells are rescued from OA toxicity by co-aggregation of OA and HEWL. Using atomic force microscopy in combination with fluorescence microscopy, we revealed that HEWL forms round-shaped aggregates in the presence of OA micelles instead of protofibrils of HEWL alone. These HEWL amyloids act as a sink for toxic OA micelles and their co-aggregate form large clumps, suggesting a protective function in amyloid and OA cytotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Tan J, Town T, Paris D, Mori T, Suo Z. Microglial Activation Resulting from CD40-CD40L Interaction After β-Amyloid Stimulation. Science. 1999; 286:2352–2355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

