A potential key mechanism in ascending aortic aneurysm development: Detection of a linear relationship between MMP-14/TIMP-2 ratio and active MMP-2
- PMID: 30794673
- PMCID: PMC6386481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212859
A potential key mechanism in ascending aortic aneurysm development: Detection of a linear relationship between MMP-14/TIMP-2 ratio and active MMP-2
Abstract
Objectives: Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) tissue levels have been associated with ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm (aTAA). As MMP-2 activation is controlled by interactions among matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14), a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) and Pro-MMP-2 in cell culture, this activation process might also play a role in aTAA.
Methods: Via gelatin zymography we analyzed tissue levels of MMP-2 isoforms (Pro-MMP-2, active MMP-2, total MMP-2) and via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA,) MMP-14,TIMP-2 and total MMP-2 tissue levels in N = 42 patients with aTAA. As controls, MMP-14 and TIMP-2 aortic tissue levels in N = 9 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery were measured via ELISA, and levels of MMP-2 isoforms in N = 11 patients via gelatin zymography.
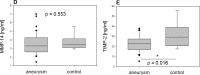
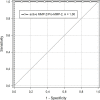
Results: Active MMP-2 was significantly higher in aTAA than in controls. Patients with aTAA exhibited significantly lower Pro-MMP-2 and TIMP-2 levels. Total MMP-2 and MMP-14 did not differ significantly between groups. Regression analysis revealed a linear relationship between TIMP-2 and the MMP-14/TIMP-2 ratio, as well as active MMP-2 in aTAA. Aneurysmatic tissue can be accurately distinguished from control aortic tissue (AUC = 1) by analyzing the active MMP-2/Pro-MMP-2 ratio with a cutoff value of 0.11, whereas MMP-14 and TIMP-2 roles are negligible in ROC analysis.
Conclusion: A larger amount of MMP-2 is activated in aTAA than in control aortic tissue-a factor that seems to be a central process in aneurysm development. When active MMP-2 exceeds 10% compared to Pro-MMP-2, we conclude that it originates from aneurysmatic tissue, which we regard as a starting point for further studies of aTAA biomarkers. The tissue's MMP-14/TIMP-2 ratio may regulate the degree of Pro-MMP-2 activation as a determining factor, while the enzymatic activities of MMP-14 and TIMP-2 do not seem to play a key role in aneurysm development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Isoforms Differ within the Aortic Wall of Ascending Aortic Aneurysms Associated with Bicuspid Aortic Valve.Cardiol Res Pract. 2020 Sep 23;2020:1306425. doi: 10.1155/2020/1306425. eCollection 2020. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33029391 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of pro-MMP-2 mediated by MT1-MMP in human salivary gland carcinomas: possible regulation of pro-MMP-2 activation by TIMP-2.J Pathol. 2004 Apr;202(4):403-11. doi: 10.1002/path.1541. J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15095267
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in ascending aortic aneurysms: bicuspid versus trileaflet aortic valves.J Surg Res. 2005 Jan;123(1):40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2004.06.007. J Surg Res. 2005. PMID: 15652949
-
Emergence of molecular imaging of aortic aneurysm: implications for risk stratification and management.J Nucl Cardiol. 2014 Apr;21(2):251-67; quiz 268-70. doi: 10.1007/s12350-013-9845-5. Epub 2014 Jan 1. J Nucl Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24381115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New indicators for systematic assessment of aortic morphology: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Jan;13(1):372-383. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2728. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 33569218 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Syndecan-1 Expression Is Increased in the Aortic Wall of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes but Is Unrelated to Elevated Fasting Plasma Glucagon-Like Peptide-1.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 20;9(6):697. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060697. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34203009 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis Identifies Crucial Genes Involved in Coronary Atherosclerotic Heart Disease.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 2;2022:6971238. doi: 10.1155/2022/6971238. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35958279 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression in skin RNA of horses affected with degenerative suspensory ligament desmitis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Oct 7;15(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01994-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33028365 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Isoforms Differ within the Aortic Wall of Ascending Aortic Aneurysms Associated with Bicuspid Aortic Valve.Cardiol Res Pract. 2020 Sep 23;2020:1306425. doi: 10.1155/2020/1306425. eCollection 2020. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33029391 Free PMC article.
-
Wall shear stress measured with 4D flow CMR correlates with biomarkers of inflammation and collagen synthesis in mild-to-moderate ascending aortic dilation and tricuspid aortic valves.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Sep 30;25(10):1384-1393. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeae130. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38748858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E, DiBartolomeo R, Eggebrecht H, et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014;35: 2873–2926. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA, Bersin RM, Carr VF, Casey DE, et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology,American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons,and Society for Vascular Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55: e27–e129. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pape LA, Tsai TT, Isselbacher EM, Oh JK, O’gara PT, Evangelista A, et al. Aortic diameter >or = 5.5 cm is not a good predictor of type A aortic dissection: observations from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation. 2007;116: 1120–1127. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.702720 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rylski B, Branchetti E, Bavaria JE, Vallabhajosyula P, Szeto WY, Milewski RK, et al. Modeling of predissection aortic size in acute type A dissection: More than 90% fail to meet the guidelines for elective ascending replacement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148: 944–948.e1. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.05.050 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274: 21491–21494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

