β-Catenin and Yes-Associated Protein 1 Cooperate in Hepatoblastoma Pathogenesis
- PMID: 30794807
- PMCID: PMC6521893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.02.002
β-Catenin and Yes-Associated Protein 1 Cooperate in Hepatoblastoma Pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Correction.Am J Pathol. 2019 Aug;189(8):1680. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.06.003. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31345468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
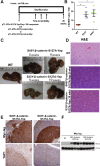
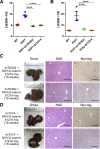
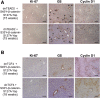
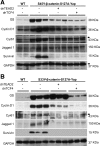
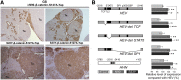
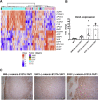
Hepatoblastoma (HB), the most common pediatric primary liver neoplasm, shows nuclear localization of β-catenin and yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) in almost 80% of the cases. Co-expression of constitutively active S127A-YAP1 and ΔN90 deletion-mutant β-catenin (YAP1-ΔN90-β-catenin) causes HB in mice. Because heterogeneity in downstream signaling is being identified owing to mutational differences even in the β-catenin gene alone, we investigated if co-expression of point mutants of β-catenin (S33Y or S45Y) with S127A-YAP1 led to similar tumors as YAP1-ΔN90-β-catenin. Co-expression of S33Y/S45Y-β-catenin and S127A-YAP1 led to activation of Yap and Wnt signaling and development of HB, with 100% mortality by 13 to 14 weeks. Co-expression with YAP1-S45Y/S33Y-β-catenin of the dominant-negative T-cell factor 4 or dominant-negative transcriptional enhanced associate domain 2, the respective surrogate transcription factors, prevented HB development. Although histologically similar, HB in YAP1-S45Y/S33Y-β-catenin, unlike YAP1-ΔN90-β-catenin HB, was glutamine synthetase (GS) positive. However, both ΔN90-β-catenin and point-mutant β-catenin comparably induced GS-luciferase reporter in vitro. Finally, using a previously reported 16-gene signature, it was shown that YAP1-ΔN90-β-catenin HB tumors exhibited genetic similarities with more proliferative, less differentiated, GS-negative HB patient tumors, whereas YAP1-S33Y/S45Y-β-catenin HB exhibited heterogeneity and clustered with both well-differentiated GS-positive and proliferative GS-negative patient tumors. Thus, we demonstrate that β-catenin point mutants can also collaborate with YAP1 in HB development, albeit with a distinct molecular profile from the deletion mutant, which may have implications in both biology and therapy.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of β-catenin and Yap1 in human hepatoblastoma and induction of hepatocarcinogenesis in mice.Gastroenterology. 2014 Sep;147(3):690-701. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 14. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24837480 Free PMC article.
-
TEA Domain Transcription Factor 4 Is the Major Mediator of Yes-Associated Protein Oncogenic Activity in Mouse and Human Hepatoblastoma.Am J Pathol. 2019 May;189(5):1077-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30794805 Free PMC article.
-
YAP1 Withdrawal in Hepatoblastoma Drives Therapeutic Differentiation of Tumor Cells to Functional Hepatocyte-Like Cells.Hepatology. 2021 Mar;73(3):1011-1027. doi: 10.1002/hep.31389. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 32452550 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of aberrant Wnt signaling in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6317-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6317. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling as a useful therapeutic target in hepatoblastoma.Biosci Rep. 2019 Sep 24;39(9):BSR20192466. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192466. Print 2019 Sep 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31511432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Help for Sick Kids: New Insights Into Hepatoblastoma.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12(1):350-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33775655 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gas1-Mediated Suppression of Hepatoblastoma Tumorigenesis.Am J Pathol. 2025 May;195(5):982-994. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2025.01.005. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Am J Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39889823
-
A MicroRNA Cluster in the DLK1-DIO3 Imprinted Region on Chromosome 14q32.2 Is Dysregulated in Metastatic Hepatoblastomas.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 12;10:513601. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.513601. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33282720 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the mechanisms of angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 14;13:1535339. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1535339. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40438141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-catenin cancer-enhancing genomic regions axis is involved in the development of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Commun. 2022 Oct;6(10):2950-2963. doi: 10.1002/hep4.2055. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Hepatol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36000549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czauderna P., Haeberle B., Hiyama E., Rangaswami A., Krailo M., Maibach R., Rinaldi E., Feng Y., Aronson D., Malogolowkin M., Yoshimura K., Leuschner I., Lopez-Terrada D., Hishiki T., Perilongo G., von Schweinitz D., Schmid I., Watanabe K., Derosa M., Meyers R. The Children's Hepatic tumors International Collaboration (CHIC): novel global rare tumor database yields new prognostic factors in hepatoblastoma and becomes a research model. Eur J Cancer. 2016;52:92–101. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perilongo G., Malogolowkin M., Feusner J. Hepatoblastoma clinical research: lessons learned and future challenges. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;59:818–821. - PubMed
-
- Czauderna P., Lopez-Terrada D., Hiyama E., Haberle B., Malogolowkin M.H., Meyers R.L. Hepatoblastoma state of the art: pathology, genetics, risk stratification, and chemotherapy. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Koch A., Denkhaus D., Albrecht S., Leuschner I., von Schweinitz D., Pietsch T. Childhood hepatoblastomas frequently carry a mutated degradation targeting box of the beta-catenin gene. Cancer Res. 1999;59:269–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

