Current Challenges and Perspectives for the Use of Aqueous Plant Extracts in the Management of Bacterial Infections: The Case-Study of Salmonella enterica Serovars
- PMID: 30795544
- PMCID: PMC6412809
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20040940
Current Challenges and Perspectives for the Use of Aqueous Plant Extracts in the Management of Bacterial Infections: The Case-Study of Salmonella enterica Serovars
Abstract
Worldwide, foodborne diseases are a growing public health problem. Among the infectious bacteria, non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars (NTS) are the major cause of hospitalization and death, and the emergence and spread of their antibiotic-resistance is becoming a worldwide health issue. This, coupled with the restrictions of antibiotics use in agriculture and animal production, calls for alternative approaches to solve this problem. Plant-derived aqueous extracts compounds could provide novel straightforward approaches to control pathogenic bacteria. This review discusses the antimicrobial activity of aqueous plant extracts against Salmonella serovars, the possible mechanisms of action involved, which components/structures might be responsible for such activity, and the current challenges for the use of these extracts/components in Salmonella infection management and their application perspectives.
Keywords: Salmonella serovars; antimicrobial activity; aqueous plant extracts; bioactive components.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
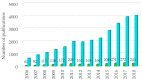
 ”antimicrobial Salmonella extract” OR “antibacterial Salmonella extract”, and
”antimicrobial Salmonella extract” OR “antibacterial Salmonella extract”, and  ”antimicrobial extract” OR “antibacterial extract” in topic, from 2006 to 2018, via Web of ScienceTM.
”antimicrobial extract” OR “antibacterial extract” in topic, from 2006 to 2018, via Web of ScienceTM.
References
-
- Radulović N.S., Blagojević P.D., Stojanović-Radić Z.Z., Stojanović N.M. Antimicrobial plant metabolites: Structural diversity and mechanism of action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013;20:932–952. - PubMed
-
- WHO Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal) [(accessed on 10 December 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal)
-
- WHO List of Antibiotic Resistant Priority Pathogens. [(accessed on 10 December 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-n...
-
- Gyawali R., Hayek S.A., Ibrahim S.A. Plant extracts as antimicrobials in food products. In: Taylor T., editor. Handbook of Natural Antimicrobials for Food Safety and Quality. Elsevier Ltd.; Cambridge, UK: 2015. pp. 49–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

