Targeting mTOR in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 30795552
- PMCID: PMC6406494
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020190
Targeting mTOR in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
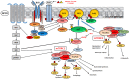
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is an aggressive hematologic disorder and constitutes approximately 25% of cancer diagnoses among children and teenagers. Pediatric patients have a favourable prognosis, with 5-years overall survival rates near 90%, while adult ALL still correlates with poorer survival. However, during the past few decades, the therapeutic outcome of adult ALL was significantly ameliorated, mainly due to intensive pediatric-based protocols of chemotherapy. Mammalian (or mechanistic) target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a conserved serine/threonine kinase belonging to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-related kinase family (PIKK) and resides in two distinct signalling complexes named mTORC1, involved in mRNA translation and protein synthesis and mTORC2 that controls cell survival and migration. Moreover, both complexes are remarkably involved in metabolism regulation. Growing evidence reports that mTOR dysregulation is related to metastatic potential, cell proliferation and angiogenesis and given that PI3K/Akt/mTOR network activation is often associated with poor prognosis and chemoresistance in ALL, there is a constant need to discover novel inhibitors for ALL treatment. Here, the current knowledge of mTOR signalling and the development of anti-mTOR compounds are documented, reporting the most relevant results from both preclinical and clinical studies in ALL that have contributed significantly into their efficacy or failure.
Keywords: Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia; cell signalling; mTOR; metabolism; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Neri L.M., Cani A., Martelli A.M., Simioni C., Junghanss C., Tabellini G., Ricci F., Tazzari P.L., Pagliaro P., McCubrey J.A., et al. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its therapeutic potential. Leukemia. 2014;28:739–748. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.226. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous