Prognostic Factors of Early Stage Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
- PMID: 30795566
- PMCID: PMC6406698
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16040637
Prognostic Factors of Early Stage Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
Abstract
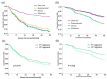
We aimed to determine prognostic factors of early stage (I/II) epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) including clinicopathologic and chemotherapeutic regimens. Four hundred and thirty-seven women who underwent primary staging surgery with adjuvant chemotherapy between January 1, 2000 and December 31, 2010 were retrospectively reviewed and analyzed from two medical centers. The prognostic factors were determined from multivariate survival analyses using Cox regression models. The majority of women were diagnosed with stage Ic (244/437, 55.8%). The histopathologic types were clear cell (37.5%), endometrioid (27.2%), serous (14.0%), and mucinous (13.3%). Fifty-seven percent (249/437) of the women received taxane-based (platinum plus paclitaxel) regimens and 43.0% received non-taxane (platinum plus cyclophosphamide) regimens as frontline adjuvant chemotherapy. Clear cell tumors (adjusted Hazard ratio (aHR) 0.37, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.21⁻0.73, p = 0.001) showed better 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) than serous tumors. Women diagnosed at FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) stage II (aHR 5.97, 95% CI = 2.47⁻14.39, p < 0.001), grade 3 tumor without clear cell (aHR 2.28, 95% CI = 1.02⁻5.07, p = 0.004) and who received 3⁻5 cycles of non-taxane regimens (aHR 3.29, 95% CI = 1.47⁻7.34, p = 0.004) had worse 5-year overall survival (OS). Clear cell histology treated with taxane-based regimens showed significantly higher 5-year DFS (91.2% vs. 82.0%, aHR = 0.45, 95% CI = 0.21⁻0.93, p = 0.043) and 5-year OS (93.5% vs. 79.0%, aHR = 0.30, 95% CI = 0.13⁻0.70, p = 0.005) than those treated with non-taxane-based regimens. We conclude that stage, tumor grade, and chemotherapeutic regimens/cycles are independent prognostic factors for early stage ovarian cancer.
Keywords: disease-free survival; histologic type; ovarian cancer; overall survival; platinum; taxane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bamias A., Sotiropoulou M., Zagouri F., Trachana P., Sakellariou K., Kostouros E., Kakoyianni K., Rodolakis A., Vlahos G., Haidopoulos D., et al. Prognostic evaluation of tumour type and other histopathological characteristics in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer treated with surgery and paclitaxel/carboplatin chemotherapy: Cell type is the most useful prognostic factor. Eur. J. Cancer. 2012;48:1476–1483. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.09.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pectasides D., Fountzilas G., Aravantinos G., Kalofonos C., Efstathiou H., Farmakis D., Skarlos D., Pavlidis N., Economopoulos T., Dimopoulos M.A. Advanced stage clear-cell epithelial ovarian cancer: The Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group experience. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006;102:285–291. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.12.038. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

