Prognostic value of performance status in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30795756
- PMCID: PMC6385458
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5375-0
Prognostic value of performance status in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The association between performance status (PS) and the prognosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the prognostic value of PS in mRCC patients treated with TKIs.
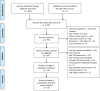
Methods: Electronic databases were searched to identify the studies that had assessed the association between pretreatment PS and prognosis in mRCC patients receiving TKIs. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) from eligible studies were used to calculate combined HRs. The heterogeneity across the included studies was assessed by Cochrane's Q test and I2 statistic. The Begg's funnel plot and Egger's linear regression teats were used to evaluate the potential publication bias. The meta-analysis was performed with RevMan 5.3 and Stata SE12.0 according to the PRISMA guidelines.
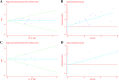
Results: A total of 6780 patients from 19 studies were included in this meta-analysis. The results showed that a poor PS was an effective prognostic factor of both OS (pooled HR: 2.08, 95% CI: 1.78-2.45) and PFS (pooled HR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.20-1.91). Subgroup analysis revealed that poor PS significantly associated with poor OS and PFS in studies using Karnofsky PS scale (OS, pooled HR: 2.20, 95% CI: 1.65-2.94; PFS, pooled HR: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.19-2.56), conducted in Asia (OS, pooled HR: 2.25, 95% CI: 1.71-2.95; PFS, pooled HR: 1.73, 95% CI: 1.14-2.64) and Newcastle-Ottawa Scale score of 8 (OS, pooled HR: 2.61, 95% CI: 1.92-3.55; PFS, pooled HR: 2.43, 95% CI: 1.36-4.33).
Conclusions: This study suggests that a poor PS is significantly associated with poor prognosis in mRCC patients receiving TKIs.
Keywords: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; Mete-analysis; Performance status; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the procedures performed were in full accordance with the ethical standards of the appropriate national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration. This study was approved by the institution Ethics Commission of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital and the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University. The need for consent to participate was waived by Ethics Commission of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital and the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
C-reactive protein is a predictor of prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Dec;475:178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 29080691
-
Hypertension as a prognostic factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Urol. 2019 Jun 7;19(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12894-019-0481-5. BMC Urol. 2019. PMID: 31174518 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-lymphocyte ratio acts as an independent predictor of prognosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 May;480:166-172. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.02.014. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29462592
-
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of prognosis in renal carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):44039-44046. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9836. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27270655 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Urol. 2020 Jul 6;20(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00665-8. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32631294 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TRAF2 promotes M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage infiltration, angiogenesis and cancer progression by inhibiting autophagy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 6;42(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02742-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37415241 Free PMC article.
-
Improved functional assessment in cancer patients using home-based digital technologies.Sci Rep. 2025 May 21;15(1):17638. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02401-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40399391 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Immunity Gene Expression Patterns and Machine Learning Approaches in Association with Response to Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors-Based Treatments in Clear-Cell Renal Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;15(23):5637. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235637. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067341 Free PMC article.
-
To Treat or Not to Treat? Dilemmas when Deciding on Antineoplastic Treatment in Patients With Far Advanced Cancers.Cancer Control. 2023 Jan-Dec;30:10732748231176639. doi: 10.1177/10732748231176639. Cancer Control. 2023. PMID: 37178323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geriatric-assessment-identified functional deficits among adults with multiple myeloma with normal performance status.J Geriatr Oncol. 2022 Mar;13(2):182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2021.08.004. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Geriatr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34389255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29. - PubMed
-
- Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ, Russell MW, Charbonneau C. Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): a literature review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;34(3):193–205. - PubMed
-
- Thomas JS, Kabbinavar F. Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a review of current therapies and novel immunotherapies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;96(3):527–533. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):115–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

